Key Points:
- Neural interfaces facilitate direct communication between the brain and external devices.
- Advancements in non-invasive BCIs offer practical applications in healthcare, gaming, and various industries.
- Ethical considerations and privacy concerns are critical as neural interfaces become more prevalent.
- Ongoing research and development promise unprecedented possibilities in human-machine collaboration.
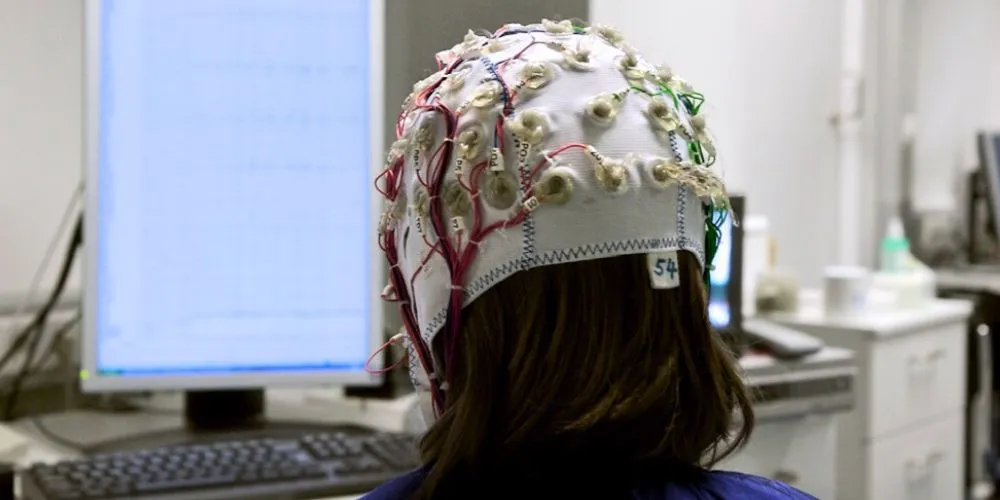
Recent strides in neural interfaces are revolutionizing human-machine interaction, ushering in a new era of technological possibilities. Neural interfaces, also known as brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), enable direct communication between the brain and external devices, opening avenues for enhanced control, communication, and cognitive augmentation.
These interfaces leverage the intricate connection between the brain and technology, enabling seamless interaction with devices. One of the groundbreaking aspects of neural interfaces is their potential to restore mobility and communication for individuals with paralysis or neurological disorders. Researchers and companies are developing BCIs that enable users to control prosthetic limbs, navigate computer interfaces, or even type messages through direct brain signals.
The emergence of non-invasive neural interface technologies is a notable development, eliminating the need for surgical implants. Wearable devices with electroencephalogram (EEG) sensors capture brain activity and translate it into actionable commands. This has practical applications across fields, from healthcare to gaming, where users can operate devices or play games via neural commands.
Moreover, neural interfaces are making significant strides in virtual and augmented reality. By deciphering neural signals related to movement and intention, BCIs enhance the immersive experience in virtual environments. This has implications for gaming and extends to training simulations, medical procedures, and architectural design.
Healthcare is witnessing the integration of neural interfaces in novel ways. Researchers are exploring BCIs for treating conditions such as chronic pain, depression, and epilepsy. These interfaces enable precise neuromodulation, offering an alternative or complementary approach to traditional treatments.
As neural interfaces advance, ethical considerations and privacy concerns emerge. Ensuring the security of neural data and addressing potential misuse are critical aspects that researchers and policymakers are actively addressing. Striking a balance between innovation and securing user privacy is paramount as these technologies become more prevalent.
Neural interfaces represent a transformative force in human-machine collaboration, with applications ranging from medical breakthroughs to immersive technologies. This field’s ongoing research and development promise to unlock unprecedented possibilities, shaping a future without boundaries between the human brain and technology.