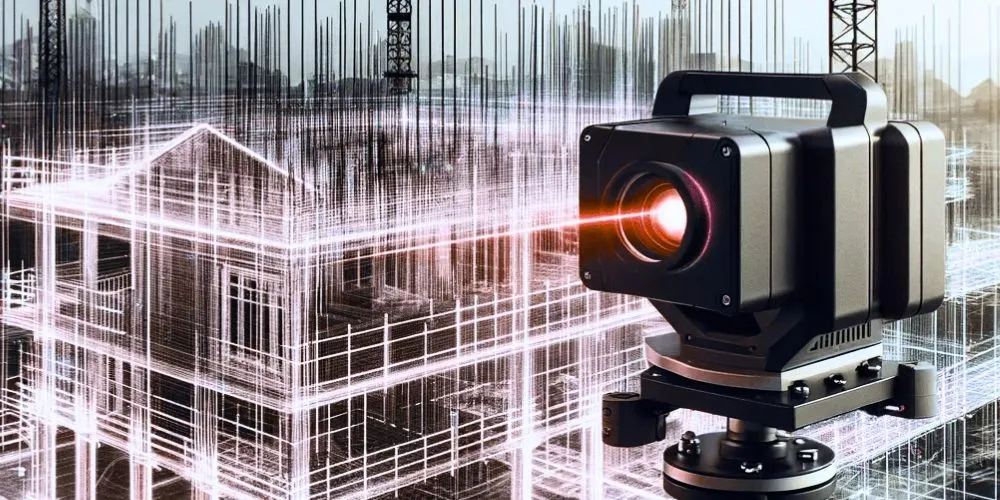
Laser scanning technology has emerged as a transformative force across various industries, providing unparalleled mapping and 3D visualization precision. In an era where detailed spatial data is crucial for decision-making and project execution, the integration of laser scanning is paramount. This comprehensive exploration delves into laser scanning technology, uncovering its significance, applications across various sectors, and its transformative potential for creating a more accurate, efficient, and informed landscape.
The Significance of Laser Scanning Technology
Laser scanning technology represents a groundbreaking shift in how spatial data is collected, analyzed, and visualized. These systems provide organizations with the tools and technology needed to capture highly accurate 3D data quickly and efficiently. This shift towards more precise data acquisition carries substantial implications, from improved asset management to enhanced safety and innovation.
Precision Data Acquisition
One primary benefit of laser scanning technology is its ability to capture highly precise spatial data. Laser scanners emit laser beams that bounce off surfaces and return to the scanner, allowing for the creation of detailed 3D point clouds. This level of precision is unmatched by traditional surveying methods, enabling organizations to capture accurate representations of physical spaces and objects.
Efficiency and Time Savings
Laser scanning technology significantly reduces the time required for data acquisition. Traditional surveying methods involve time-consuming fieldwork, whereas laser scanning can rapidly capture vast amounts of data in a single scan. This newfound efficiency accelerates project timelines, reduces labor costs, and minimizes disruptions to ongoing operations.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
Safety is paramount in various industries, and laser scanning technology is critical in risk mitigation. By capturing accurate spatial data remotely, organizations can avoid sending personnel into potentially hazardous environments. This proactive approach enhances safety by minimizing exposure to dangerous conditions and ensuring that assets are inspected and maintained without jeopardizing human safety.
Techniques in Laser Scanning Technology
Laser scanning technology encompasses a variety of techniques and tools to enhance data acquisition and visualization.
Terrestrial Laser Scanning
Terrestrial laser scanning involves using ground-based scanners to capture data from stationary positions. These scanners emit laser beams in various directions, creating a comprehensive 3D point cloud of the scanned area. This technique captures data in indoor and outdoor environments and large-scale projects such as construction and archaeological site documentation.
Mobile Laser Scanning
Mobile laser scanning employs scanners mounted on vehicles or drones to capture data as they move through an area. This technique is suitable for mapping road networks, railways, and infrastructure corridors. It allows for rapid data acquisition and is particularly useful for monitoring environmental changes over time.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
LiDAR is a remote sensing technique that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D models of the surveyed area. It is widely used in topographic mapping, forestry, and autonomous vehicle applications. LiDAR technology provides accurate elevation data and is crucial for floodplain modeling, urban planning, and disaster management.
Applications of Laser Scanning Technology
Laser scanning technology finds application across diverse sectors, each reaping the rewards of precise mapping and 3D visualization.
Architecture and Construction
In architecture and construction, laser scanning technology aids in site analysis, building documentation, and quality control. Architects and engineers use laser scans to create detailed 3D models of existing structures and environments, facilitating renovation and remodeling projects. Laser scanning also helps construction teams monitor progress and ensure building components align with design specifications.
Surveying and Land Management
Land surveyors use laser scanning technology to create accurate topographic maps, land boundary surveys, and cadastral records. These maps are essential for urban planning, land development, and land management. Laser scanning improves the accuracy of land surveys and provides valuable data for zoning decisions and environmental impact assessments.
Cultural Heritage Preservation
Laser scanning plays a crucial role in cultural heritage preservation by documenting historical sites, monuments, and artifacts with unmatched precision. These digital replicas aid in conserving and restoring cultural heritage, allowing researchers and historians to study and digitally preserve fragile or inaccessible artifacts.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the adoption of laser scanning technology holds immense promise, it also presents challenges and ethical considerations that necessitate careful consideration.
Data Privacy and Security
Collecting and storing highly detailed spatial data raises concerns about privacy and security. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or cyber threats is essential. Organizations must implement robust data encryption, access controls, and data management protocols to safeguard laser scanning data.
Ethical Data Use
Laser scanning data should be used ethically and responsibly. Organizations must respect privacy and cultural sensitivities when scanning and sharing spatial data, especially in culturally significant or private locations. Ethical considerations ensure that laser scanning technology benefits society without infringing on individuals’ rights or cultural heritage.
Environmental Impact
Evaluating the environmental impact of laser scanning technology is essential. Sustainable manufacturing and responsible disposal practices for laser scanning equipment are vital to minimize its carbon footprint. Manufacturers and users of laser scanning technology should explore opportunities to reduce their environmental impact and promote eco-friendly practices.
The Future of Laser Scanning Technology
Laser scanning technology is poised to assume an even more substantial role in shaping the future of data acquisition and visualization, fostering precision, efficiency, and innovation.
Integration with Augmented Reality
Laser scanning with augmented reality (AR) will enhance data visualization and analysis. AR technologies allow users to overlay laser scanning data onto the physical world, providing real-time insights and enhancing decision-making in construction, architecture, and urban planning.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Applying artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to laser scanning data will enable automated data analysis and pattern recognition. AI algorithms can detect anomalies, identify trends, and extract valuable information from large datasets. It will streamline data interpretation and provide actionable insights across various industries.
Urban Planning and Smart Cities
Laser scanning technology will be crucial in urban planning and the development of smart cities. Accurate 3D models of urban environments will support efficient infrastructure development, transportation planning, and disaster resilience. Laser scanning will also be integral to creating digital twins, allowing cities to simulate and optimize urban systems.
Conclusion
Laser scanning technology is not merely a tool for data acquisition; it is a transformative force that enhances precision mapping and 3D visualization across diverse industries. Its significance lies in its capacity to provide organizations with highly accurate spatial data, empowering them to make informed decisions that lead to better project outcomes. As laser scanning technology evolves, ethical considerations, data privacy, and environmental impact must guide its development and deployment.
They envision a future where precision data acquisition is a cornerstone of decision-making, innovation is driven by accurate 3D visualization and laser scanning technology contributes positively to society, culture, and the environment. Laser scanning is the key to unlocking new mapping, planning, and analysis possibilities, ultimately leading to a more informed and interconnected world. With laser scanning technology, industries are poised to create a future where precision meets innovation—one scan at a time.