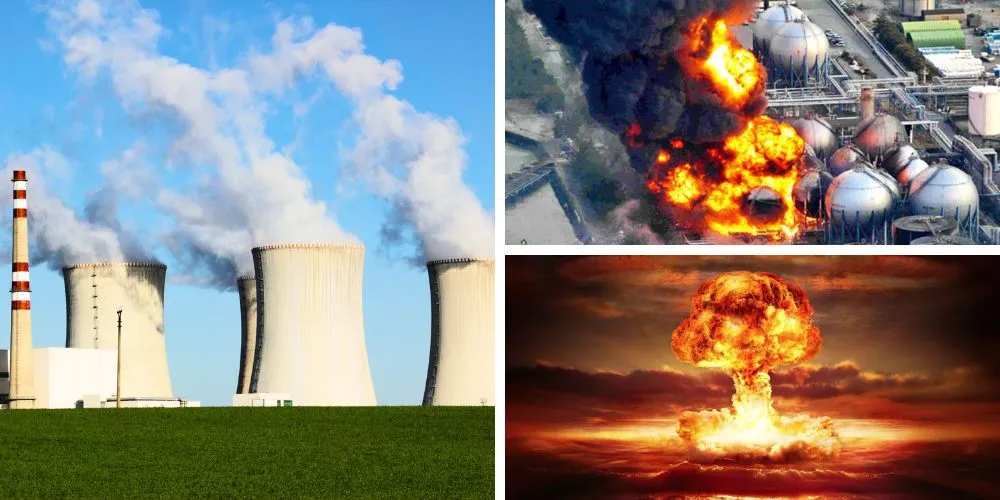
Nuclear power plants are formidable symbols of human ingenuity and technological advancement in energy production. Yet, their existence raises profound questions about safety, sustainability, and ethical stewardship. As we contemplate the role of nuclear power plants in our energy landscape, it is imperative to reflect on the wisdom they offer, the ethical considerations they evoke, and the balance between risk and reward in their utilization.
Nuclear power plants harness the immense power of nuclear fission to generate electricity on a massive scale, providing a reliable and relatively low-carbon energy source. They play a crucial role in diversifying our energy portfolio, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and mitigating climate change. This technological feat prompts us to marvel at humanity’s ability to harness the forces of nature for the betterment of society, underscoring the potential of nuclear energy to meet our growing needs.
However, the operation of nuclear power plants is not without risks and ethical dilemmas. The specter of nuclear accidents, such as the Chornobyl disaster and the Fukushima Daiichi meltdown, looms large in our collective consciousness, reminding us of the catastrophic consequences of nuclear mishaps. Wisdom calls us to acknowledge these risks with humility and vigilance, urging us to prioritize safety, rigorous regulatory oversight, and transparent communication in the management of nuclear facilities.
Furthermore, nuclear power plants generate radioactive waste that poses significant environmental and health hazards, necessitating careful management and disposal. The ethical implications of nuclear waste storage raise questions about intergenerational equity, environmental justice, and long-term stewardship.
Wisdom compels us to confront these challenges with foresight and integrity, advocating for sustainable solutions that minimize harm to both people and the planet. It calls for interdisciplinary collaboration, public engagement, and ethical deliberation in shaping policies and practices related to nuclear waste management.
Moreover, nuclear power plants have geopolitical implications, as the proliferation of nuclear technology raises concerns about nuclear weapons proliferation and international security. The dual-use nature of nuclear technology underscores the importance of global cooperation, arms control agreements, and diplomatic efforts to prevent the misuse of nuclear materials. Wisdom urges us to prioritize diplomacy, nuclear non-proliferation, and disarmament initiatives, recognizing that pursuing peace and security is inseparable from the responsible stewardship of nuclear technology.
Nuclear power plants represent a double-edged sword in our energy security and sustainability quest. As we navigate the complexities of nuclear energy, let us do so with wisdom, humility, and a commitment to ethical principles. Let us harness the potential of nuclear technology while remaining vigilant to its risks, striving to strike a delicate balance between innovation and responsibility. Doing so can pave the way for a more just and sustainable energy future.