Sustainable urban planning has emerged as a critical paradigm shift in city development, advocating for environmentally conscious, socially equitable, and economically viable urban landscapes. This article explores the multifaceted realm of sustainable urban planning, delving into its fundamental principles, diverse methodologies, key advantages, notable applications, and the challenges it addresses within the dynamic landscape of modern urbanization and infrastructure.
Unveiling Sustainable Urban Planning
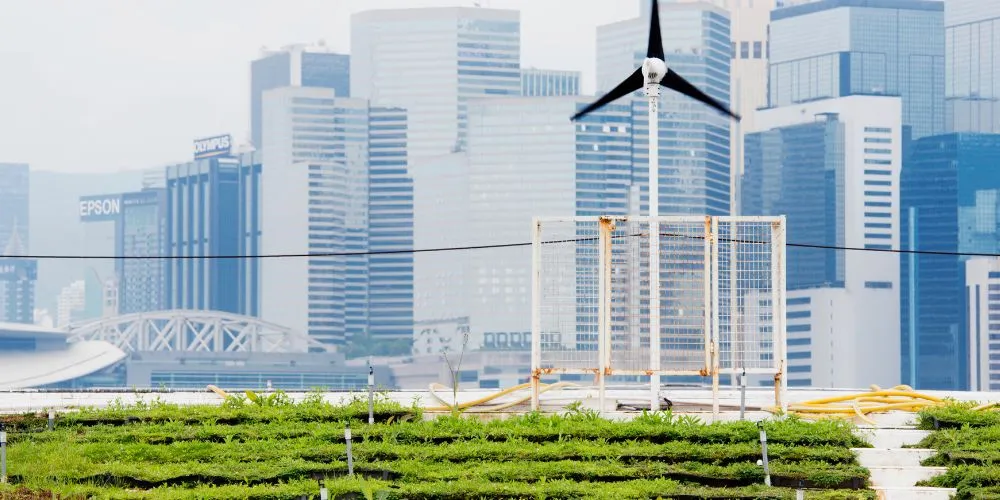
Sustainable urban planning is a holistic approach to city development that prioritizes environmental sustainability, social inclusivity, and economic resilience. It seeks to create urban spaces that are not only environmentally friendly but also foster community well-being and economic prosperity. This form of urban planning recognizes the interdependence of ecological, social, and economic factors, aiming to balance the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Key Components of Sustainable Urban Planning
Understanding the key components of sustainable urban planning is essential for comprehending its complexity and impact:
- Green Infrastructure: Green infrastructure, including parks, urban forests, and green corridors, is integral to sustainable urban planning. These elements enhance biodiversity, provide recreational spaces for residents, and contribute to overall environmental resilience.
- Mixed-Use Zoning: It promotes mixed-use zoning, allowing for diverse activities within a given area. This approach reduces reliance on automobiles, encourages walking and cycling, and creates vibrant, walkable neighborhoods.
- Public Transportation: Prioritizing public transportation is key to sustainable urban planning. Efficient and accessible public transit systems reduce traffic congestion, lower carbon emissions, and enhance the overall mobility of urban populations.
- Energy-Efficient Buildings: It encourages the development of energy-efficient buildings. From green roofs to passive design principles, incorporating sustainable features into urban structures helps reduce energy consumption and lower the environmental footprint.
Methodologies of Sustainable Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning employs various methodologies to create urban spaces that align with environmental, social, and economic sustainability:
- Smart City Technologies: Smart city technologies leverage data and digital infrastructure to enhance urban efficiency. These technologies, from smart grids to intelligent transportation systems, contribute to resource optimization and improved urban management.
- Community Engagement: Involving communities in the planning process is crucial to achieving sustainable urban development. Engaging residents ensures that the planning process is inclusive, responsive to local needs, and promotes a sense of ownership and belonging.
- Brownfield Redevelopment: Brownfield redevelopment involves repurposing vacant or underutilized industrial sites. It often transforms these areas into mixed-use developments, reducing urban sprawl and revitalizing neglected urban spaces.
Advantages of Sustainable Urban Planning
The adoption of sustainable urban planning brings forth a multitude of advantages, reshaping how cities are designed, developed, and experienced:
Environmental Resilience and Biodiversity Preservation
One of the primary advantages of sustainable urban planning is its emphasis on environmental resilience and biodiversity preservation. Green spaces, sustainable infrastructure, and thoughtful land-use planning contribute to preserving ecosystems within urban environments.
Improved Quality of Life for Residents
It significantly improves the quality of life for urban residents. Access to green spaces, efficient public transportation, and reduced pollution contribute to healthier and more enjoyable urban living experiences.
Economic Prosperity and Job Creation
Sustainable urban planning stimulates economic prosperity and job creation. Investments in green infrastructure, renewable energy projects, and energy-efficient buildings generate employment opportunities and attract businesses committed to sustainable practices.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
It is crucial in mitigating and adapting to climate change. By incorporating climate-resilient design, promoting the use of renewable energy, and reducing carbon emissions, cities can contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
Applications of Sustainable Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning finds applications across diverse urban contexts, influencing how cities address challenges and envision their futures:
Eco-Districts for Comprehensive Sustainability
Eco-districts exemplify sustainable urban planning on a smaller scale. These districts focus on integrated approaches to sustainability, incorporating energy-efficient buildings, green infrastructure, and community engagement to create holistic and eco-friendly urban neighborhoods.
Transit-Oriented Developments for Efficient Mobility
Transit-oriented developments prioritize efficient mobility by concentrating housing, businesses, and amenities around transit nodes. This approach encourages walking, cycling, and public transportation, reducing reliance on private cars and minimizing traffic congestion.
Urban Renewal Projects for Sustainable Revitalization
Urban renewal projects embrace sustainable urban planning to revitalize existing urban areas. It often involves repurposing underutilized spaces, improving infrastructure, and promoting mixed-use developments that breathe new life into urban neighborhoods.
Green Building Initiatives for Energy-Efficient Structures
Green building initiatives are crucial components of sustainable urban planning. By promoting energy-efficient construction, sustainable materials, and green design practices, cities can reduce their carbon footprint and enhance the overall sustainability of their built environments.
Challenges in Sustainable Urban Planning
While the advantages are evident, the practice of sustainable urban planning faces its own set of challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of sustainable urban development:
Balancing Economic Growth and Sustainability Goals
One of the challenges in sustainable urban planning is striking a balance between economic growth and sustainability goals. Cities must navigate the tension between development pressures and the imperative to adopt eco-friendly practices.
Infrastructure Retrofitting in Established Cities
Retrofitting existing infrastructure in established cities poses challenges. Adapting older buildings, upgrading transportation systems, and integrating sustainable practices into established urban contexts require careful planning and significant investments.
Inclusive Community Engagement and Social Equity
Ensuring inclusive community engagement and social equity is challenging in sustainable urban planning. The planning process must prioritize the needs of all residents, address social disparities, and avoid gentrification that can displace vulnerable communities.
Future Trends in Sustainable Urban Planning
As technology continues to evolve, future trends in sustainable urban planning point toward advancements that further enhance its capabilities:
Smart Infrastructure for Connected Cities
The integration of smart infrastructure is a future trend in sustainable urban planning. It includes smart grids, intelligent transportation systems, and data-driven management tools that optimize resource use and enhance urban efficiency.
Nature-Based Solutions for Urban Resilience
Nature-based solutions, such as green roofs, urban forests, and water-sensitive urban design, are gaining prominence. It may increasingly incorporate these solutions to enhance urban resilience against climate change and natural disasters.
Circular Economy Principles for Urban Resource Management
Adopting circular economy principles is a future trend to promote sustainable resource management in cities. It involves minimizing waste, maximizing resource efficiency, and fostering a circular flow of materials within urban environments.
Participatory Technologies for Inclusive Planning
Participatory technologies are emerging as tools for inclusive planning and decision-making. Virtual reality, augmented reality, and online platforms can facilitate broader community engagement in the urban planning process.
Conclusion
Sustainable urban planning stands at the forefront of reimagining the future of cities, emphasizing resilience, sustainability, and inclusivity. Its ability to integrate environmental considerations with social and economic priorities positions it as a transformative force in the evolution of urban spaces. While challenges persist, ongoing advancements and future trends indicate a dynamic and promising future for sustainable urban planning, with applications extending into new frontiers of resilient, eco-friendly, and socially vibrant urban landscapes.