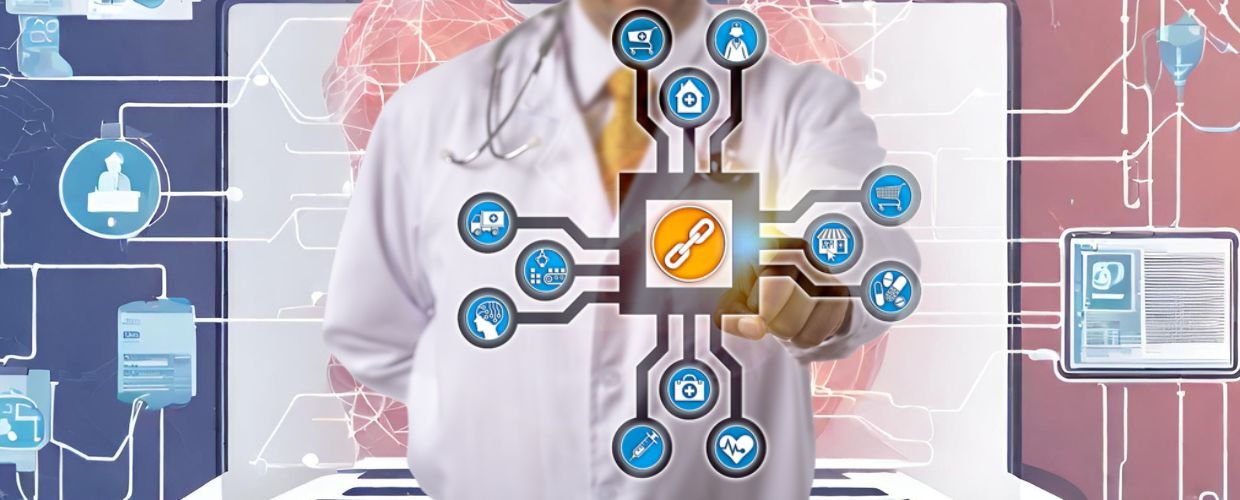
Originally designed for cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation that could revolutionize the healthcare industry. In an era marked by the digitization of healthcare data and the increasing importance of data security and interoperability, this comprehensive exploration delves into blockchain in healthcare, unveiling its significance, diverse applications, and transformative potential for creating a more secure, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem.
The Significance of Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain in healthcare technology significantly shifts how healthcare data is stored, accessed, and shared. Its decentralized and immutable nature offers numerous advantages, including enhanced security, interoperability, and data integrity, which are paramount in healthcare settings.
Data Security and Privacy
One of the foremost concerns in healthcare is the security and privacy of patient data. Blockchain’s cryptographic techniques and decentralized structure make it exceptionally resilient to cyberattacks and unauthorized access. Patient data stored on a blockchain is tamper-proof and can only be accessed by authorized individuals, ensuring the utmost privacy.
Interoperability and Data Exchange
The lack of interoperability among healthcare systems has long been a hurdle to seamless data exchange. Blockchain’s ability to establish a standardized, secure, real-time data exchange protocol can break down these silos, allowing healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient records regardless of the source.
Patient-Centric Control
Blockchain in healthcare empowers patients to have greater control over their health data. Patients can grant or revoke access to their records, decide which parts of their data to share, and participate in research initiatives, fostering a more patient-centric approach to healthcare.
Techniques in Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain’s capabilities in healthcare are made possible through various techniques and technologies that ensure data security, privacy, and transparency.
Decentralization and Distributed Ledger
Blockchain in healthcare operates on a decentralized computer network, often called nodes. These nodes collectively maintain a distributed ledger that records all transactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of a single point of failure.
Cryptographic Encryption
Blockchain employs cryptographic encryption techniques to secure data. Each transaction is encrypted, and a consensus mechanism is used to validate and add transactions to the blockchain. This encryption ensures that patient data remains confidential and unaltered.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions. In healthcare, smart contracts can automate processes such as insurance claims, ensuring that claims are processed accurately and transparently. They also reduce administrative overhead and minimize the potential for fraudulent claims.
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain has many applications across various healthcare domains, significantly improving patient care, data management, and supply chain tracking.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Blockchain enhances the security and accessibility of electronic health records (EHRs). Patients can have a single, comprehensive EHR accessible by authorized healthcare providers, streamlining care coordination and reducing the likelihood of medical errors arising from incomplete or outdated information.
Drug Traceability and Supply Chain Management
Blockchain ensures the authenticity and integrity of pharmaceutical products by tracking their journey from the manufacturer to the patient. This transparency reduces the risk of counterfeit drugs entering the market and enhances patient safety, particularly in the case of critical medications and vaccines.
Clinical Trials and Research
Blockchain facilitates the transparent and secure management of clinical trial data. Researchers can securely access and verify data integrity, accelerating the research process and improving the reliability of research findings. It heightened transparency and instilled greater confidence in the outcomes of clinical trials, contributing to more robust evidence-based medicine.
Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
The integration of blockchain into telemedicine platforms offers secure and private remote consultations. Patients can have virtual appointments with healthcare providers while ensuring the confidentiality of their health data. This broadens healthcare access and protects sensitive patient information during telehealth interactions.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The adoption of blockchain in healthcare introduces challenges and ethical considerations that demand careful attention and mitigation.
Scalability and Energy Consumption
Blockchain networks can face scalability issues, particularly when dealing with large healthcare transactions. Additionally, the energy consumption associated with blockchain mining, especially in proof-of-work systems, can be a concern for sustainability. Efforts are underway to develop more efficient consensus mechanisms and scaling solutions to address these challenges.
Regulatory Compliance
The healthcare industry is heavily regulated, and blockchain must comply with existing laws and regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Ensuring blockchain implementations meet regulatory standards while preserving privacy and security is a complex challenge requiring collaboration between technology providers and regulatory bodies.
Ethical Use of Health Data
The ethical use of health data on a blockchain is paramount. Patients must maintain control over their data and be fully informed about its use. Critical ethical considerations are ensuring transparency, informed consent, and clear data ownership rights. Additionally, blockchain applications must be designed to minimize the risk of data re-identification or unintended data leakage.
The Future of Blockchain in Healthcare
Blockchain technology is poised to continue shaping the future of healthcare with innovative applications and approaches that enhance data security, interoperability, and patient engagement.
Improved Healthcare Data Exchange
Blockchain’s ability to establish a secure, standardized data exchange protocol will improve healthcare data interoperability. It will enable seamless sharing of patient information across healthcare providers and systems, ultimately improving patient care, reducing duplication of tests and procedures, and streamlining administrative processes.
Healthcare Data Marketplaces
Blockchain can facilitate the creation of healthcare data marketplaces where patients can share their data for research purposes in exchange for compensation or other benefits. This approach incentivizes patients to participate in medical research while ensuring data privacy and security. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies can access a more extensive and diverse pool of patient data for drug discovery, clinical trials, and epidemiological studies.
Global Health Data Exchange
Blockchain can facilitate secure global health data exchange, allowing healthcare providers worldwide to access critical patient information during emergencies, pandemics, or when traveling abroad. It ensures that travelers receive appropriate care regardless of location and contributes to more effective public health responses.
Conclusion
Blockchain in healthcare is not just a technological innovation but a transformative force that addresses some of the industry’s most pressing challenges. Its significance lies in enhancing data security, interoperability, and patient control over health records. As blockchain technology evolves, it must be guided by ethical considerations, regulatory compliance, and scalability solutions to ensure responsible and effective implementation.
It envisions a future where healthcare data is secure, accessible, and patient-centric, ultimately leading to improved patient care, streamlined processes, and a more efficient and transparent healthcare ecosystem. Blockchain in healthcare represents a fundamental shift towards a healthcare system prioritizing data security, patient empowerment, and collaborative healthcare delivery.