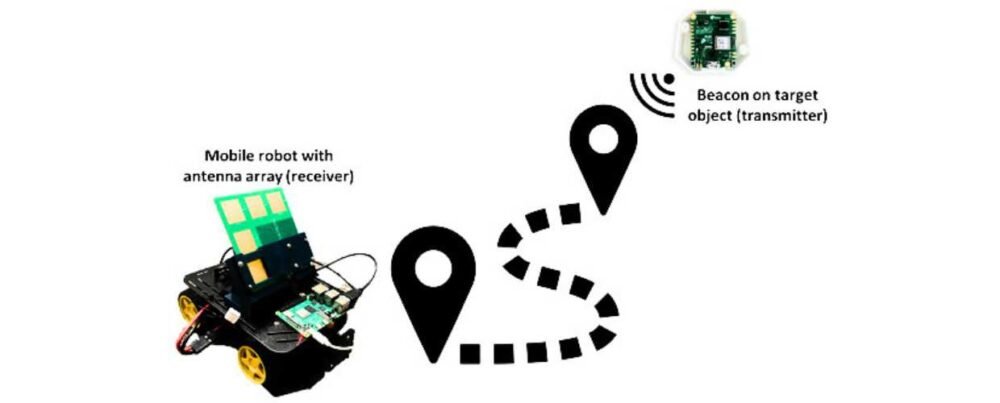
Two researchers, Katrina Weinmann and Steve Simske, from Colorado State University, proposed a Bluetooth homing controller solution for an autonomous mobile robot and provided details on the controller’s structure and implementation.
Advancements in Autonomous Robot Navigation
The progress of autonomous robot navigation technologies has revolutionized the deployment of mobile robots in complex and uncertain real-world settings. A crucial aspect of autonomous navigation involves guiding a robot to a location determined in real-time, even if it is previously unknown and situated within its vicinity. This capability holds particular significance for indoor environments where traditional localization technologies like GPS fail to provide the required accuracy for precise target locations.
Bluetooth 5.1 AoA-Based Controller for Homing
In this research, the researchers introduced a novel controller design tailored to steer a mobile robot toward an object whose location is initially unknown, leveraging Bluetooth 5.1 Angle of Arrival (AoA) technology. The proposed setup integrates a Bluetooth beacon onto the target object and deploys a Bluetooth antenna array onto the mobile robot. This arrangement establishes a communication link between the robot and the target object. The controller’s core function is to facilitate the homing process of the mobile robot towards the object, relying on the precision of Bluetooth 5.1 AoA technology for accurate direction determination.
Hybrid Approach for Precise Position Estimation
The designed controller adopts a hybrid approach that amalgamates two distinct methodologies for calculating and refining the estimated target position. This hybridization incorporates parallax and vector position calculations derived from Bluetooth Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) data. Through simulations, the efficacy of the controller is meticulously assessed under varying levels of sensor noise. The results consistently converge toward accurate target positions, demonstrating a mean accuracy of 0.12 meters or less in environments with and without obstacles. The versatility of the proposed controller is evident as it can either function as a standalone controller, directly directing robot motion toward the target, or seamlessly integrate with other existing robot navigation techniques by providing the target position as an output.
The fusion of Bluetooth 5.1 Angle of Arrival technology and the innovative controller design marks a significant stride in mobile robot navigation. Enabling robots to navigate toward previously unknown locations within real-world environments paves the way for more effective indoor navigation and opens possibilities for applications across various industries. The simulation-backed validation underscores the accuracy and potential of this approach, highlighting its capacity to augment both standalone robot navigation and broader navigation strategies.