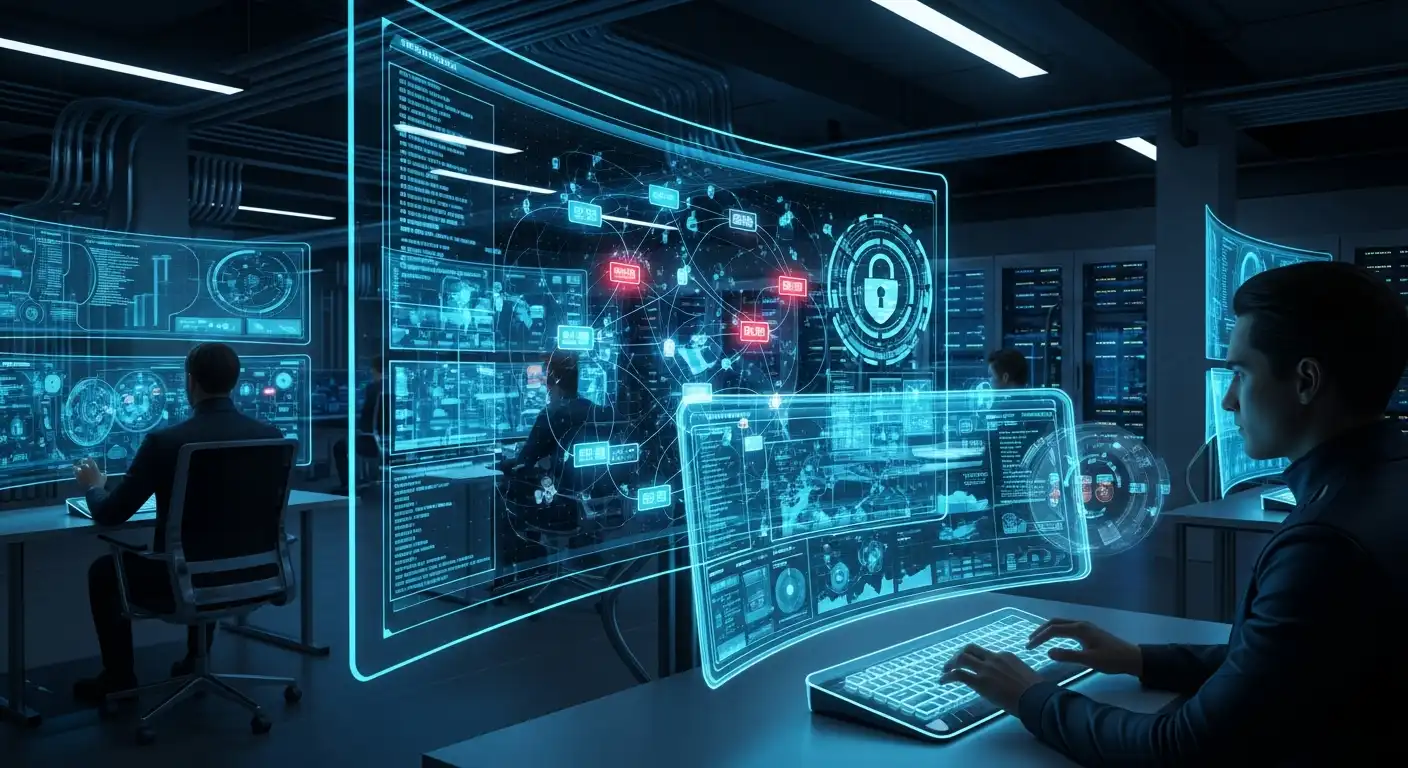
Cyber warfare has emerged as a critical aspect of modern conflict, encompassing digital techniques and technologies to wage war in cyberspace. It involves various strategies, tactics, and operations designed to compromise and manipulate digital systems and networks.
Cyber Warfare Facts
Some facts regarding cyber warfare are presented below.
- Types of Cyber Attacks: Malicious software (malware) is designed to damage or gain unauthorized access to systems. Attempts to deceive individuals or organizations into revealing sensitive information and to overwhelm a system or network, rendering it unavailable to users. She coordinated and targeted cyber attacks, often state-sponsored, aimed at long-term infiltration.
- Targets of Cyber Warfare: Cyber threats target government systems, corporate networks, and critical infrastructure, causing unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruption, thereby affecting national security, business integrity, and public services.
- Cyber Weapons: These are software tools or exploits used to carry out cyberattacks. Examples include Stuxnet, a computer worm that targeted Iran’s nuclear program, and WannaCry, a ransomware attack that affected organizations globally.
- International Laws and Norms: The absence of clear international laws and norms governing cyber warfare poses a significant challenge to effectively addressing cyber threats and holding perpetrators accountable.
- Preventive Measures: Implementing cybersecurity measures, conducting regular updates, providing employee training, and engaging in international cooperation are crucial for defending against cyber warfare.
Cyber Warfare Views
Addressing this multifaceted challenge requires a comprehensive approach involving governments, the private sector, academia, and international organizations.
- National Security Concerns: Governments and security experts regard cyber warfare as a significant threat to national security, given its potential to disrupt critical infrastructure and exfiltrate sensitive information.
- Economic Impact: Cyberattacks can have severe economic consequences, affecting businesses, financial institutions, and entire economies. The cost of cyberattacks, in terms of financial losses and recovery efforts, is a growing concern.
- Privacy and Civil Liberties: Balancing the need for cybersecurity with privacy and civil liberties is a key concern. Enhanced cybersecurity measures may infringe on privacy rights, prompting debates about the right balance.
- Need for Global Cooperation: Many advocate international cooperation and collaboration to establish effective global cyber norms, treaties, and agreements that mitigate cyber threats.
- Role of Technology Industry: Some emphasize the technology industry’s role in developing secure systems and advocating for responsible use of technology to prevent and promote ethical practices.
Conclusion
Cyber warfare is a rapidly evolving domain that demands continuous adaptation and innovation in cybersecurity strategies. Establishing clear international laws and norms, advancing technology, promoting cybersecurity awareness, and fostering global cooperation are critical to effectively managing and mitigating the threats posed by cyber warfare.