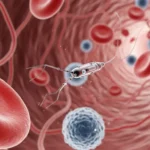
In healthcare, nanoparticles have emerged as a groundbreaking tool, offering unprecedented possibilities for diagnostics, drug delivery, and therapy. This article explores the extensive realm of nanoparticles in medicine, highlighting their significance, tracing the development of key technologies, examining various applications, and envisioning the transformative potential they hold for the future of healthcare.
The Significance of Nanoparticles in Medicine
Nanoparticles in medicine represent a paradigm shift, providing a versatile platform for precise diagnosis and targeted drug delivery. Their unique properties at the nanoscale offer advantages such as increased surface area, tunable reactivity, and the ability to navigate biological barriers, making them invaluable in the quest for more effective and personalized medical interventions.
Targeted Drug Delivery and Enhanced Efficacy
One of the key significances of nanoparticles in medicine is their ability to revolutionize drug delivery. Nanoparticles can be engineered to rapidly transport therapeutic agents to specific cells or tissues, enabling targeted treatment while minimizing side effects. This targeted drug delivery enhances the efficacy of treatments for various diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, and neurological disorders.
Imaging and Diagnostics
Nanoparticles play a crucial role in advancing medical imaging and diagnostics. Contrast agents utilize nanoparticles to enhance the resolution of imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), and positron emission tomography (PET). Additionally, nanoparticles can be functionalized for molecular imaging, enabling the visualization of specific biological targets.
Overcoming Biological Barriers
Nanoparticles excel in overcoming biological barriers that often limit the effectiveness of traditional therapies. For example, they can cross the blood-brain barrier, helping deliver drugs to the brain to treat neurological disorders. This capability expands the scope of medical interventions and opens avenues for addressing previously untreatable conditions.
Evolution of Key Technologies in Nanoparticles for Medicine
The journey of nanoparticles in medicine is intricately woven with technological advancements that have revolutionized drug delivery systems and diagnostic tools.
Liposomal Drug Delivery
Liposomes, nanoscale vesicles composed of lipid bilayers, have pioneered nanoparticle drug delivery technology. These nanocarriers protect therapeutic agents, facilitate their controlled release, and can be engineered to target specific cells or tissues. Liposomal formulations have proven particularly effective in cancer therapy, improving drug delivery to tumor sites.
Polymeric Nanoparticles
Polymeric nanoparticles offer a versatile platform for drug delivery due to their biocompatibility and tunable properties. These nanoparticles can be designed to release drugs in response to specific triggers, such as changes in pH or enzymatic activity, providing controlled and sustained release profiles that enhance therapeutic outcomes.
Quantum Dots for Imaging
Quantum dots, semiconductor nanocrystals, have found applications in medical imaging due to their unique optical properties. These nanoscale fluorophores emit bright, stable signals, making them valuable for fluorescence imaging. Quantum dots can improve the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic imaging techniques.
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Iron oxide nanoparticles serve as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Their magnetic properties alter the relaxation times of nearby water molecules, enhancing the contrast in MR images. These nanoparticles are employed in liver imaging, vascular imaging, and the detection of inflammatory conditions.
Diverse Applications of Nanoparticles in Medicine
Nanoparticles in medicine have diverse applications, ranging from targeted drug delivery to innovative diagnostic tools, reshaping the landscape of medical interventions.
Cancer Therapy and Targeted Drug Delivery
Nanoparticles have revolutionized cancer therapy by enabling the targeted delivery of drugs to tumor cells. Functionalized nanoparticles can selectively accumulate in the tumor tissue, delivering therapeutic agents directly to cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues. This approach minimizes side effects and enhances the overall effectiveness of cancer treatments.
Infectious Disease Treatment
In the realm of infectious diseases, nanoparticles offer new avenues for treatment. Antimicrobial nanoparticles can combat bacteria, viruses, and fungi, providing an alternative to traditional antibiotics. Additionally, nanoparticles can be utilized for targeted delivery of antiviral agents, enhancing the efficiency of antiviral therapies.
Neurological Disorders and Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing
Nanoparticles hold promise for treating neurological disorders by overcoming the blood-brain barrier. Functionalized nanoparticles can cross this barrier, enabling the delivery of therapeutic agents to the brain. This breakthrough has implications for the treatment of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and brain tumors.
Personalized Medicine and Theranostics
Nanoparticles play a crucial role in the realization of personalized medicine through theranostics, which combines therapy and diagnostics. Multifunctional nanoparticles can carry therapeutic agents, imaging agents, and targeting moieties within a single nanosystem. This integrated approach enables real-time monitoring of treatment responses and personalized adjustments to therapeutic regimens.
Transformative Possibilities and Future Outlook
The trajectory of nanoparticles in medicine points towards a future filled with continued innovation, integration, and unprecedented possibilities.
Gene Therapy and RNA Delivery
Nanoparticles are poised to play a crucial role in advancing gene therapy. Nanocarriers can deliver genetic material, such as RNA, to target cells, opening avenues for treating genetic disorders, cancer, and other conditions at the genetic level. It can tailor precision medicine to an individual’s genetic profile.
Immunotherapy and Nanoparticle Vaccines
Nanoparticles are contributing to the development of nanoparticle vaccines and immunotherapeutic strategies. Engineered nanoparticles can enhance the delivery of antigens and adjuvants, optimizing the immune response. This approach is transforming the landscape of vaccine development and cancer immunotherapy.
Regulatory Guidelines and Standardization
As nanoparticles in medicine evolve, establishing regulatory guidelines and standardization becomes crucial. Ensuring the safety, efficacy, and reproducibility of nanoparticle-based therapies requires clear frameworks for assessment, approval, and monitoring. Standardization efforts will contribute to the responsible integration of nanomedicine into clinical practice.
Conclusion
Nanoparticles in medicine have evolved from a conceptual idea to a transformative force with far-reaching implications for the healthcare industry. As we navigate the nanoworld, the significance of nanoparticles in medicine is both promising and profound. With continued research, technological breakthroughs, and a commitment to responsible applications, nanoparticles will continue to be a driving force in reshaping how we diagnose, treat, and envision the future of medical interventions.