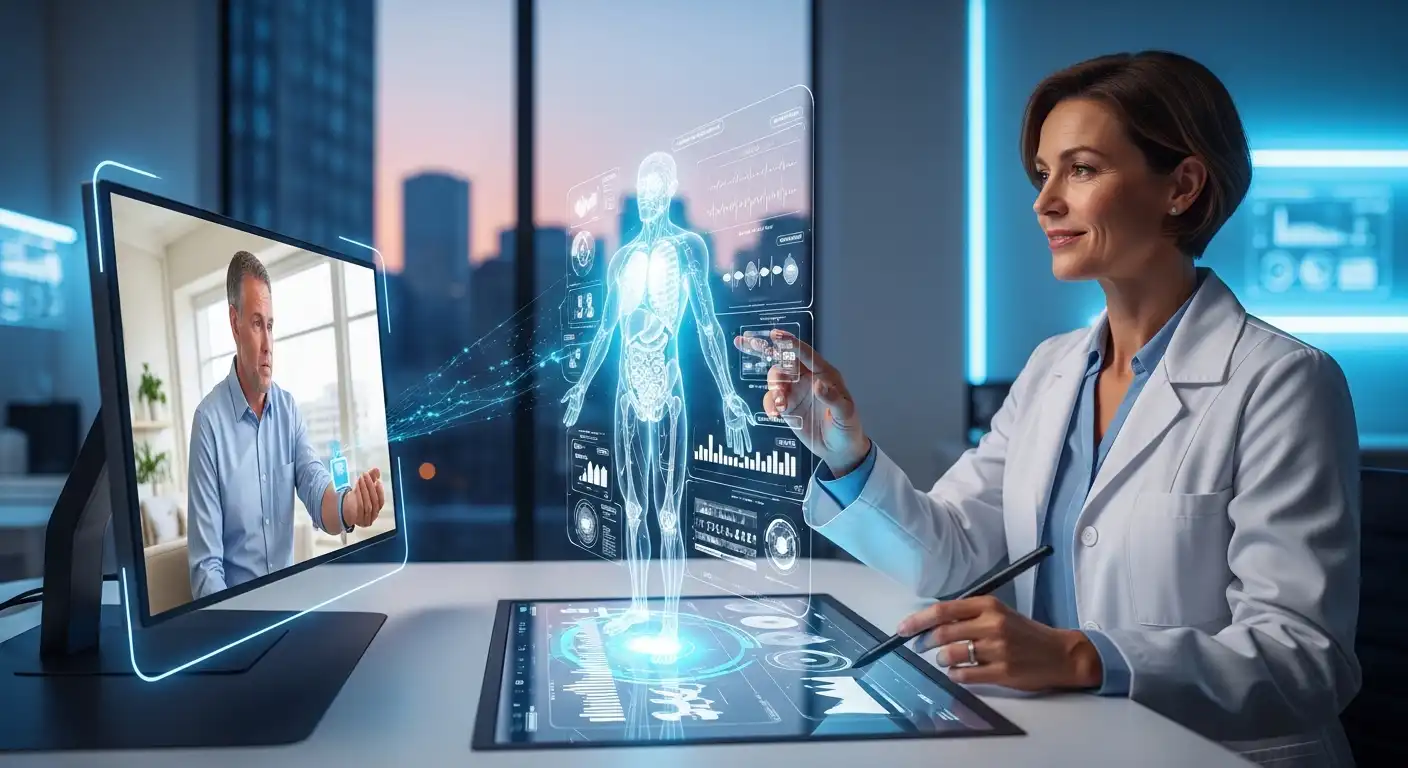
In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, remote diagnostics is a transformative force, leveraging advanced technology to bring medical expertise beyond traditional healthcare settings. This article explores the significance of remote diagnostics, its evolution, applications, challenges, and its profound impact on reshaping healthcare service delivery.
Significance of Remote Diagnostics in Healthcare
Remote diagnostics is pivotal in extending healthcare services beyond the confines of physical clinics and hospitals. By harnessing digital technologies, such as telemedicine and connected devices, healthcare providers can remotely assess, monitor, and diagnose patients, offering timely interventions and improving access to medical expertise.
Access to Healthcare in Remote Areas
One of the primary significances of remote diagnostics is its ability to address healthcare disparities by providing access to medical services in remote and underserved areas. Through telemedicine platforms, individuals in geographically isolated regions can connect with healthcare professionals, receive diagnostic services, and access timely medical advice, thereby bridging healthcare access gaps.
Timely Intervention and Chronic Disease Management
It enables timely intervention and chronic disease management by continuously monitoring patients’ health metrics. Connected devices, wearable technology, and remote monitoring tools empower individuals to track vital signs, allowing healthcare providers to detect early warning signs, adjust treatment plans, and prevent complications, improving overall patient outcomes.
Minimizing Healthcare Costs and Burden
The use of remote diagnostics has the potential to reduce healthcare costs by reducing the need for frequent in-person visits, hospital readmissions, and unnecessary emergency department visits. Efficient remote monitoring can enable proactive healthcare management, thereby preventing costly complications and optimizing resource allocation within the healthcare system.
Evolution of Remote Diagnostics
The evolution of remote diagnostics is closely tied to advances in telecommunications, digital health technologies, and the increasing interconnectivity of devices.
Telemedicine Platforms and Virtual Consultations
The advent of telemedicine platforms has been a cornerstone in the evolution of remote diagnostics. Virtual consultations enable healthcare providers to assess patients remotely, discuss symptoms, review medical histories, and prescribe treatments, thereby creating a more convenient and accessible healthcare experience.
Wearable Technology and Remote Monitoring Devices
The integration of wearable technology and remote monitoring devices has significantly contributed to the evolution of remote diagnostics. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical-grade devices enable individuals to monitor vital signs, track health metrics, and share real-time data with healthcare providers, facilitating continuous remote assessment.
Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare
The Internet of Things (IoT) has enhanced remote diagnostics. Connected medical devices, such as blood pressure monitors, glucose meters, and ECG monitors, communicate seamlessly with healthcare systems, allowing for real-time data transmission, analysis, and remote interpretation by healthcare professionals.
Applications of Remote Diagnostics in Healthcare
Remote diagnostics finds diverse applications across various healthcare domains, influencing primary care, specialized consultations, and the management of chronic conditions.
Telecardiology and Remote ECG Monitoring
Cardiology enables telecardiology services and remote ECG monitoring. Patients with cardiovascular conditions can wear portable ECG devices, and the data is transmitted to healthcare providers for real-time analysis, allowing for prompt intervention and adjustments to treatment plans.
Teledermatology and Skin Condition Assessments
Teledermatology leverages remote diagnostics to assess skin conditions. Patients can capture images of skin lesions or rashes using smartphones or digital cameras, which are then transmitted to dermatologists for remote evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations.
Remote Pulmonary Function Monitoring
It enables monitoring of pulmonary function in individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Integrated spirometers and respiratory devices enable healthcare providers to assess lung function and adjust treatment plans remotely.
Challenges in Remote Diagnostics
While remote diagnostics offers significant benefits, it also faces challenges related to technology adoption, data security, and the need for standardized practices.
Technology Adoption and Digital Divide
Adopting remote diagnostic technologies may be hindered by challenges related to access to technology, digital literacy, and the digital divide. Ensuring equitable access to technology and promoting digital literacy are essential for realizing the full potential of remote diagnostics.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
It involves transmitting and storing sensitive health data, raising concerns about data security and patient privacy. Implementing robust encryption, secure communication channels, and compliance with privacy regulations is critical to building trust in remote diagnostic platforms.
Standardization of Practices and Regulations
The standardization of remote diagnostic practices and regulatory frameworks is a challenge that the healthcare industry must address. Establishing common standards for data exchange, interoperability, and regulatory compliance will facilitate the seamless integration and widespread adoption of remote diagnostics.
Future Directions of Remote Diagnostics
The future of remote diagnostics holds exciting possibilities, including advancements in artificial intelligence, expanded use of connected devices, and integration of remote diagnostics into routine healthcare practices.
Artificial Intelligence for Diagnostic Assistance
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into remote diagnostics will enhance accuracy and efficiency. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and assist healthcare providers in interpreting diagnostic images, thereby facilitating more precise and timely diagnoses.
Expanded Use of Remote Monitoring Devices
As technology continues to evolve, the use of remote monitoring devices to track various health parameters will expand. Innovations in sensor technology, miniaturization, and battery life will contribute to the development of more accessible and user-friendly remote diagnostic devices.
Integration into Routine Healthcare Practices
The future of remote diagnostics involves seamless integration into routine healthcare practices. As telemedicine and remote monitoring become integral components of healthcare delivery, healthcare providers will incorporate remote diagnostics as standard tools for assessing, diagnosing, and managing various health conditions.
Conclusion
Remote diagnostics represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, making medical expertise more accessible, convenient, and proactive. As technology advances, the integration of remote diagnostics into routine healthcare practices holds the promise of improving health outcomes, reducing disparities in access to care, and optimizing healthcare system efficiency. Overcoming challenges and embracing future innovations will ensure that they continue to play a central role in shaping the future of healthcare.