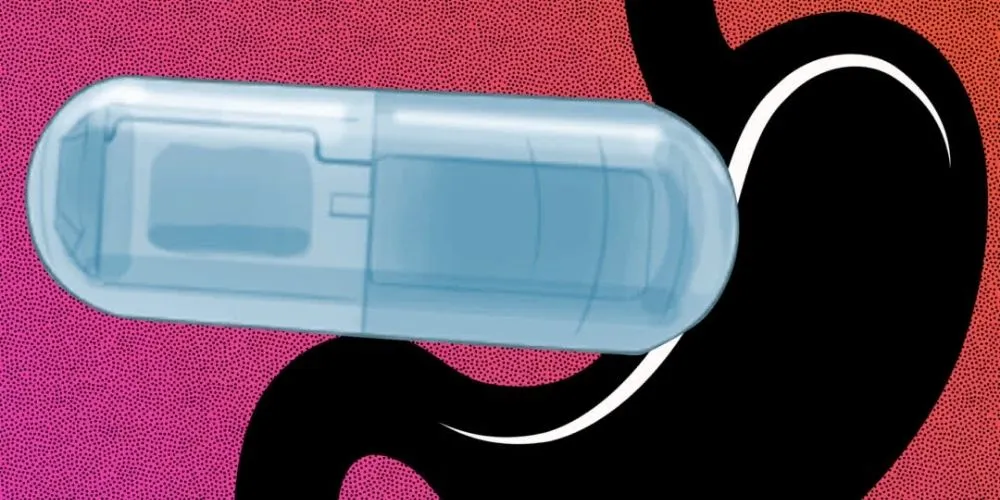
MIT researchers have introduced an innovative approach to tackle obesity using an ingestible capsule that vibrates within the stomach, creating an illusion of fullness. The capsule, equipped with a vibrating element, activates stretch receptors in the stomach, prompting the release of satiety hormones.
In animal studies, this treatment led to a remarkable 40% reduction in food intake when administered 20 minutes before meals. The researchers believe that if further studies prove its safety and efficacy in humans, the vibrating pill could provide a minimally invasive and cost-effective solution to combat obesity.
The concept leverages the body’s natural response to stomach distension, where mechanoreceptors sense stretching and send signals to the brain via the vagus nerve. This process triggers the release of hormones such as insulin, C-peptide, Pyy, and GLP-1, collectively contributing to digestion, a feeling of fullness, and decreased appetite. The vibrating pill aims to mimic this process artificially by stimulating stretch receptors through vibrations.
The capsule, roughly the size of a multivitamin, is activated by gastric fluids upon reaching the stomach, dissolving a gelatinous membrane, and completing the electronic circuit. Powered by a small silver oxide battery, the pill vibrates for 30 minutes, mirroring the post-meal hormone release patterns. The researchers observed that animals treated with the vibrating pill consumed 40% less food, resulting in slower weight gain than untreated periods.
MIT researchers, including lead author Shriya Srinivasan and senior author Giovanni Traverso, envision the pill as a potential alternative to existing obesity treatments, which can be invasive or financially inaccessible. The nonmedical intervention could be ingested before each meal, offering a unique and affordable option for individuals seeking weight loss or appetite control. The researchers aim to explore wireless on/off capabilities for prolonged use and plan to scale up manufacturing for future clinical trials in humans.
Traverso emphasized the potential of this novel approach, stating, “The behavioral change is profound, and that’s using the endogenous system rather than any exogenous therapeutic.” The team’s vibrating pill opens possibilities for transforming obesity care, especially in global health settings where cost-effective and accessible treatment options are crucial. The research received funding from the National Institutes of Health, Novo Nordisk, and the National Science Foundation.