In pursuing sustainable and energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions, geothermal heat pumps have emerged as a powerful technology, utilizing the Earth’s natural heat to provide comfort for residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. This article explores the principles behind geothermal heat pumps, their environmental benefits, applications, and their transformative potential in the quest for a more sustainable HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) industry.
Understanding Geothermal Heat Pumps
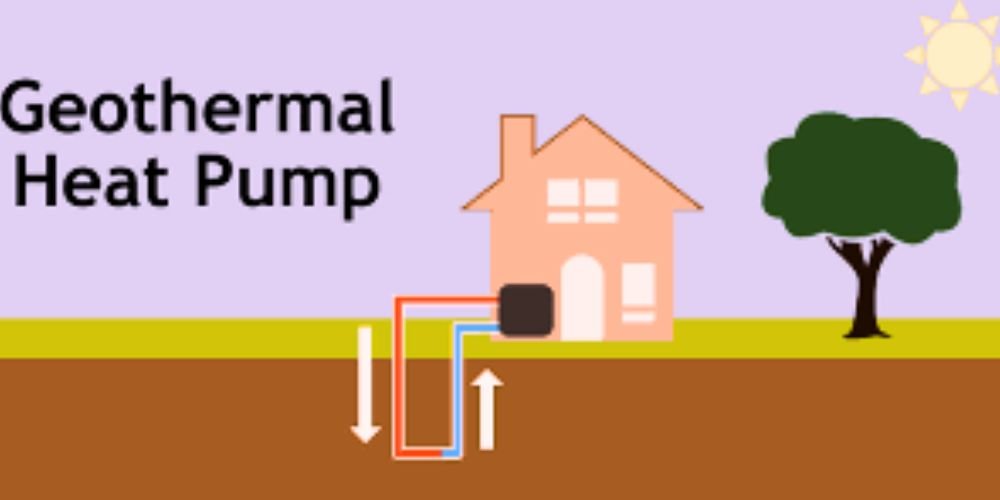
Geothermal heat pumps, also known as ground-source heat pumps, leverage the stable temperature of the Earth’s subsurface to heat efficiently and cool buildings. Unlike traditional HVAC systems that depend on external air, they extract heat from or dissipate heat into the ground, providing a more consistent and energy-efficient solution.
How Geothermal Heat Pumps Work
Geothermal heat pumps operate on the principle that the Earth’s subsurface maintains a relatively constant temperature throughout the year. In winter, the pumps remove heat from the ground and transfer it to the building’s interior. In summer, the process is reversed, with the pumps extracting heat from the building and depositing it into the cooler ground.
Components of Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pump systems have three main components: the ground loop, heat pump unit, and air delivery system. The ground loop, typically made of high-density polyethylene piping, circulates a fluid (usually water or antifreeze) to exchange heat with the ground. The heat pump unit contains a compressor, heat exchanger, and refrigerant to facilitate the heat exchange. The air delivery system broadcasts the conditioned air throughout the building.
Environmental Benefits of Geothermal Heat Pumps
Adopting geothermal heat pumps has significant environmental benefits, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and overall energy consumption.
High Energy Efficiency
Geothermal heat pumps are renowned for their high energy efficiency. By tapping into the Earth’s stable temperature, these systems need less energy to heat or cool spaces than traditional HVAC systems. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and reduced carbon footprints.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Relying on renewable geothermal energy reduces the want for fossil fuels, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions. They are crucial in mitigating climate change by offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to conventional heating and cooling systems.
Low Operating Costs
While the upfront costs of installing geothermal heat pump systems may be higher, the long-term operational costs are generally lower. The energy savings achieved through efficient heating and cooling contribute to cost-effectiveness over the system’s lifespan, making it an economically possible and environmentally friendly investment.
Applications of Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps find versatile applications across various sectors, offering efficient and sustainable heating and cooling solutions for different environments.
Residential Heating and Cooling
In residential settings, it provides homeowners with a reliable and energy-efficient solution for heating and cooling. These systems can be installed in new constructions or retrofitted into existing homes, offering year-round comfort with reduced environmental impact.
Commercial and Industrial Buildings
Geothermal heat pumps scale effectively to meet commercial and industrial buildings’ heating and cooling demands. Their adaptability makes them suitable for various applications, including office spaces, warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and data centers.
Educational Institutions and Government Facilities
Schools, universities, and government buildings can benefit from geothermal heat pump systems’ energy efficiency and environmental advantages. These applications align with sustainability goals and contribute to creating energy-responsible public infrastructure.
Transformative Potential and Future Outlook
Geothermal heat pumps hold transformative potential in shaping the future of HVAC technology and contributing to a more sustainable and resilient built environment.
Advancements in Technology
Ongoing research and development in geothermal heat pump technology aim to enhance efficiency, reduce installation costs, and expand the applicability of these systems. Innovations in materials, heat exchange mechanisms, and control systems contribute to continuously improving geothermal HVAC solutions.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Geothermal heat pumps can be incorporated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to create hybrid systems. This integration further enhances energy sustainability and resilience, creating a comprehensive approach to renewable energy utilization.
Increased Awareness and Adoption
As environmental awareness grows and the demand for sustainable building solutions rises, the adoption of geothermal heat pumps is expected to increase. Government incentives, energy efficiency regulations, and public awareness campaigns will likely drive the widespread adoption of this technology in the coming years.
Conclusion
Geothermal heat pumps represent a sustainable and efficient solution for heating and cooling, offering a glimpse into the future of environmentally responsible HVAC technology. By harnessing the Earth’s natural energy, these systems contribute to reduced energy consumption, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and long-term cost savings. As technology continues to evolve and the global focus on sustainability intensifies, geothermal heat pumps are a transformative force in creating a more sustainable and resilient built environment for future generations.