Key Points
- Nanomedicine is poised to transform healthcare by enabling personalized, minimally invasive treatments.
- Nanotechnology enables high-accuracy targeting of specific cells, genes, and molecules.
- Nanoparticles can deliver medications directly to affected sites, thereby improving treatment efficacy and reducing side effects, particularly in cancer therapy.
- It can be used for early disease detection by binding to specific biomarkers, thereby aiding the proactive diagnosis of conditions such as cancer and heart disease.
In a groundbreaking leap towards personalized and minimally invasive healthcare, nanomedicine has emerged as a beacon of hope. It promises to revolutionize how we diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases. This burgeoning field is poised to reshape the healthcare landscape, combining the precision of nanotechnology with the intricacies of medical science.
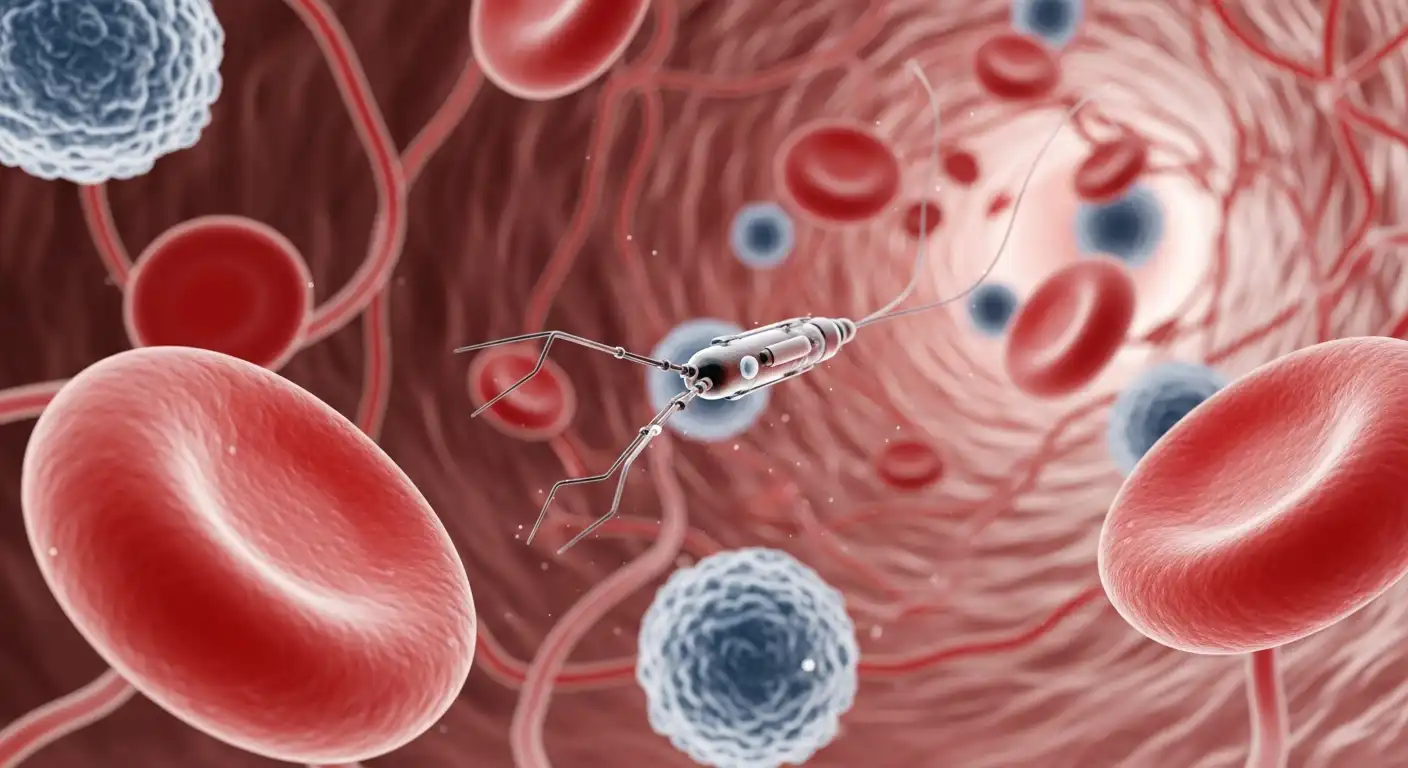
Imagine a world in which diseases are intercepted and eliminated at their very inception, without the need for invasive surgeries or potent drugs. Nanomedicine, combining nanotechnology and medicine, is making this vision a reality. Doctors can now target specific cells, genes, and even individual molecules with unprecedented accuracy by manipulating nanoparticles on a molecular scale.
One of the most promising aspects of nanomedicine is its potential to deliver highly targeted drug therapies. Tiny nanoparticles, often smaller than individual cells, can be designed to transport medications directly to affected areas within the body. It enhances treatment efficacy and minimizes side effects by avoiding damage to healthy tissues. Imagine cancer treatments that precisely attack tumor cells while leaving surrounding healthy tissue unharmed.
Moreover, nanomedicine is poised to advance diagnostics. Nanoparticles coated with molecules that bind to specific biomarkers can be administered to the body, enabling early detection of diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and neurodegenerative disorders. This proactive approach to diagnosis holds the key to preventing potentially life-threatening conditions.
The potential of nanomedicine extends beyond the conventional realms of medicine. Researchers are exploring the integration of nanotechnology with other fields, such as artificial intelligence and robotics. Nanobots, microscopic robots, could be designed to perform intricate tasks within the body, like clearing clogged arteries or repairing damaged tissues.
However, as with any burgeoning technology, challenges lie ahead. Ensuring the safety of nanoparticles, understanding their potential environmental impacts, and addressing ethical concerns are paramount as nanomedicine approaches widespread adoption.
The future of healthcare is undeniably intertwined with the promise of nanomedicine. As research progresses and breakthroughs continue to unfold, the prospect of a world where diseases are detected and treated at the molecular level becomes increasingly tangible. With nanomedicine at the forefront, the boundaries of what is medically possible are expanding, ushering in an era of personalized, precise, and profoundly transformative healthcare.