Key Points
- Researchers developed a library of over 3 million molecular compounds for genetic disease treatment.
- A novel compound targets the Crohn’s disease-associated ATG16L1 T300A variant.
- The compound stabilizes proteins to restore normal cellular functions without degrading them.
- Researchers aim to refine the approach for animal models and broader therapeutic applications.
Over the past two decades, genetic studies have linked tens of thousands of DNA variants to numerous traits and diseases. However, effectively addressing these genetic variations has remained challenging due to the lack of precise molecular tools. The research was published in Cell Chemical Biology.
Researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Harvard University have developed a groundbreaking approach to tackling disease-related genetic variants. They have used an extensive library of over three million molecular compounds.
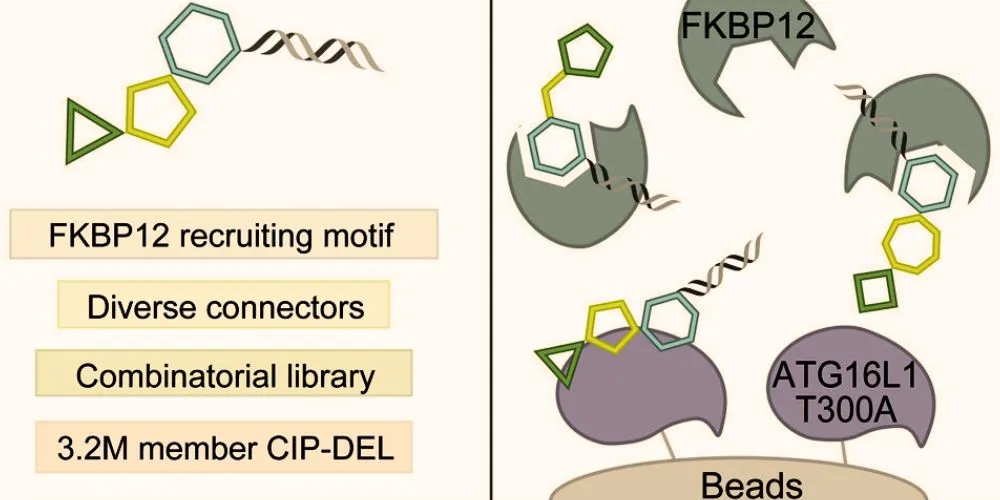
This library leverages advanced chemistry techniques to create compounds that combine two proteins, allowing one to shield and stabilize the other, thereby reversing disease-related effects. A notable achievement is identifying a compound targeting a genetic variant, ATG16L1 T300A, associated with Crohn’s disease.
The variant impairs autophagy, a cellular process essential for removing waste and harmful bacteria, by making the protein more vulnerable to enzymatic cleavage. Using their innovative compound, researchers stabilized the protein, restored autophagy, and reversed cellular impairments in human and mouse cells.
The library, known as a DNA-encoded library of chemical inducers of proximity (CIP-DEL), incorporates diverse linkers and target-binding elements, offering unmatched versatility in addressing genetic diseases. Unlike previous approaches that focused on degrading malfunctioning proteins, this method stabilizes them to restore normal function. The researchers are now exploring ways to refine the compound for use in animal models and expand its applications to other diseases.
This innovative “plug-and-play” system allows researchers to customize libraries for specific diseases and molecular mechanisms. By recruiting presenter proteins that target only affected tissues, the approach could achieve unparalleled precision in therapeutic interventions, potentially transforming how genetic diseases are treated.