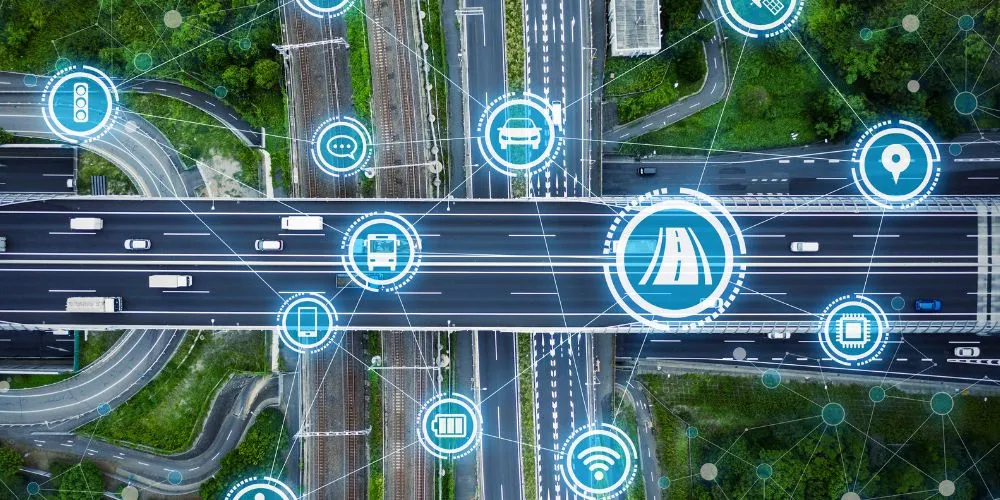
Smart transportation systems are at the forefront of the ongoing revolution in urban mobility. These innovative systems leverage cutting-edge technology to enhance transportation efficiency, reduce congestion, improve safety, and minimize environmental impact. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the world of smart transportation systems, delving into their fundamental principles and technology, discussing their potential to reshape urban mobility, and highlighting the challenges and opportunities they present for the future of transportation.
What Are Smart Transportation Systems?
Smart transportation systems encompass a wide range of technologies and strategies to make urban transportation more efficient, safe, and sustainable. These systems use real-time data, connectivity, automation, and advanced analytics to optimize various aspects of transportation, including traffic management, public transit, road safety, and environmental impact.
How Do Smart Transportation Systems Work?
Smart transportation systems rely on a network of sensors, data collection devices, communication infrastructure, and intelligent algorithms to collect, process, and act upon real-time transportation data. This data includes information from vehicles, traffic signals, public transit, and even individual smartphones. By analyzing this data, smart transportation systems can make informed decisions to improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, enhance safety, and reduce environmental impact.
Advantages of Smart Transportation Systems
Smart transportation systems offer numerous advantages that have the potential to revolutionize urban mobility.
Traffic Management
Real-time traffic data and predictive analytics enable smart transportation systems to optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and travel times. Adaptive traffic signals, dynamic lane management, and congestion pricing are examples of strategies that can be employed.
Public Transit Enhancement
Smart transportation systems improve the reliability and accessibility of public transit. Real-time transit tracking, fare payment solutions, and demand-responsive transit services make public transportation more appealing and efficient. This reduces traffic congestion and promotes the use of environmentally friendly modes of transport.
Safety Improvements
Advanced safety features such as collision avoidance systems, pedestrian detection, and connected vehicle technology enhance road safety. Smart transportation systems can alert drivers and authorities to potential hazards in real time, preventing accidents and saving lives. Integrating safety measures also includes monitoring vehicle maintenance and ensuring that vehicles are in optimal condition.
Environmental Benefits
Smart transportation systems can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution by reducing congestion and optimizing traffic flow. Promoting alternative modes of transportation, such as cycling and walking, also contributes to a more sustainable urban environment. Additionally, electric and hybrid vehicles are encouraged, reducing the carbon footprint of urban transportation.
Applications of Smart Transportation Systems
Smart transportation systems have a wide range of applications that can improve urban mobility.
Intelligent Traffic Management
Advanced traffic management systems can optimize traffic signal timing, adjust speed limits, and reroute traffic to reduce congestion. These systems can also prioritize public transit vehicles, ensuring they move efficiently through traffic.
Public Transit Integration
Smart transportation systems can integrate various modes of public transit, including buses, trains, and ride-sharing, to create a seamless and efficient transportation network. Real-time data sharing and multimodal trip planning make it easier for commuters to choose the most convenient and eco-friendly transportation options.
Connected Vehicles
Vehicles equipped with smart technology can communicate with each other and infrastructure, enhancing safety and improving traffic flow. For example, connected vehicles can share information about road conditions, traffic incidents, and potential hazards, allowing drivers to make informed decisions.
Mobility as a Service (MaaS)
MaaS platforms give users a single point of access to multiple transportation services, including public transit, ridesharing, bike-sharing, and more. MaaS simplifies the process of planning and paying for trips, making it more convenient for individuals to choose sustainable transportation options.
Challenges and Future Directions
While smart transportation systems offer immense potential, they also face challenges that must be addressed for their widespread adoption and success.
Data Privacy and Security
Collecting and sharing transportation data raises concerns about privacy and data security. Robust measures are needed to protect user data and prevent cyber threats. Strict data protection regulations and encryption technologies should be implemented to safeguard sensitive information.
Infrastructure Investment
Implementing smart transportation systems requires significant technological and infrastructure investments. Funding and political support are essential to realizing these systems’ full potential. Public-private partnerships and innovative financing models can secure the necessary resources.
Interoperability
Different cities and regions may adopt varying smart transportation technologies and standards. Ensuring interoperability between systems is crucial for a seamless transportation experience. Standardization efforts and open data platforms can facilitate collaboration and sharing among cities and regions.
Behavioral Change
Encouraging people to adopt new transportation habits and technologies can be challenging. Public education and incentives may be necessary to drive behavioral change. Governments and organizations can launch campaigns to promote the benefits of sustainable transportation and offer incentives such as reduced fares for public transit or tax incentives for electric vehicle adoption.
Conclusion
Smart transportation systems represent a transformative force in the realm of urban mobility. By harnessing technology, data, and connectivity, these systems have the potential to alleviate congestion, improve safety, and reduce environmental impact. As cities grow and face increasing transportation challenges, adopting smart transportation systems becomes advantageous and essential. Addressing challenges such as data privacy, infrastructure investment, interoperability, and behavioral change will be crucial as we navigate the future of urban mobility. Embracing smart transportation systems is a step toward more efficient, sustainable, and accessible transportation. The future of urban mobility is smart, connected, and optimized for the needs of the modern world.