In healthcare, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology, reshaping the landscape of patient care, medical research, and innovation. This article explores the significance of 3D printing in healthcare, its evolution, applications, and the transformative potential it holds for the future of medicine.
Significance of 3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing, also understood as additive manufacturing, has gained immense significance in healthcare due to its ability to create complex, customized objects layer by layer. This technology offers unprecedented opportunities to enhance patient care, surgical procedures, medical education, and the development of innovative medical devices.
Patient-Specific Medical Solutions
One of the key contributions of 3D printing in healthcare is its ability to produce patient-specific medical solutions. From anatomical models to customized implants and prosthetics, 3D printing enables the precise replication of patient anatomy, allowing for tailored treatment plans and improved surgical outcomes.
Surgical Planning and Training
Surgeons utilize 3D printing to create anatomical models that replicate specific patient cases. These models serve as invaluable instruments for surgical planning, allowing surgeons to visualize complex procedures, practice techniques, and optimize approaches before entering the operating room.
Customized Implants and Prosthetics
3D printing enables the fabrication of customized implants and prosthetics that perfectly match the patient’s anatomy. This level of customization enhances comfort, functionality, and integration, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a higher quality of life.
Evolution of 3D Printing in Healthcare
The evolution of 3D printing in healthcare has been marked by advancements in materials, technology, and the exploration of new applications across various medical disciplines.
Materials Innovation
The availability of a diverse range of 3D printing materials has expanded the scope of applications in healthcare. From biocompatible plastics to metal alloys, 3D printing materials are continually evolving to meet the specific requirements of different medical applications.
Multi-material Printing
Advancements in 3D printing technology now enable multi-material printing, allowing for the creation of complex structures with varied material properties in a single print. This capability is particularly beneficial for fabricating intricate medical devices and implants.
Bio-Printing and Tissue Engineering
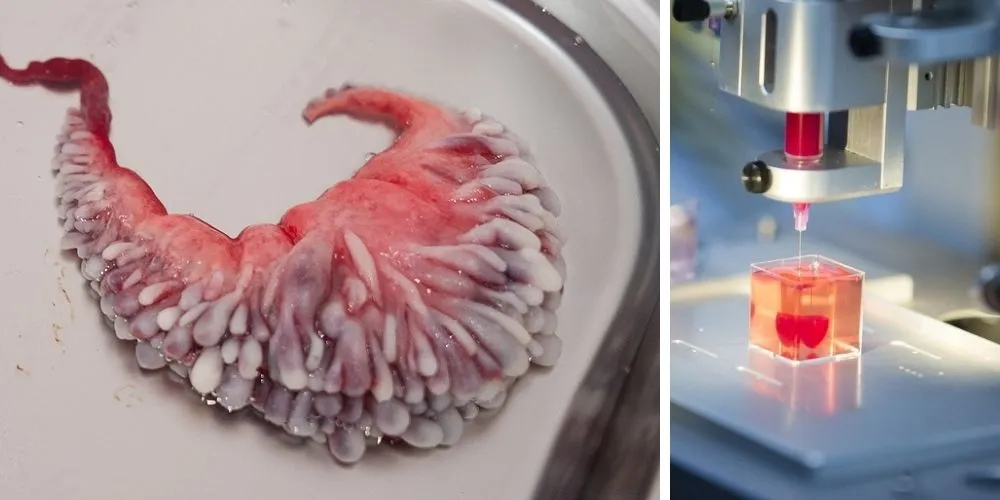
Bio-printing has emerged as a cutting-edge application of 3D printing in the healthcare sector. It involves the layer-by-layer deposition of living cells to create functional tissues and organs. While still in the early stages of development, bio-printing holds immense promise for regenerative medicine and organ transplantation.
Applications of 3D Printing in Healthcare
The applications of 3D printing in healthcare are diverse and continue to expand, encompassing a wide range of medical fields and specialties.
Anatomical Models for Surgical Planning
Surgeons utilize 3D printing to create patient-specific anatomical models based on medical imaging data. These models give a tangible representation of complex structures, facilitating preoperative planning and enhancing surgical precision.
Patient-Specific Implants and Prosthetics
Customized implants, for example, hip and knee replacements and prosthetics tailored to an individual’s anatomy, are produced through 3D printing. This customization improves implant fit, reduces the risk of complications, and enhances patient comfort.
Dental Applications
In dentistry, 3D printing is widely used to fabricate crowns, bridges, and dental prosthetics. The technology enables the creation of precise and aesthetically pleasing dental restorations, thereby improving overall oral health outcomes.
Medical Device Prototyping
Medical device manufacturers leverage 3D printing for rapid prototyping of new devices. It accelerates the product development cycle, allowing for iterative design improvements and efficient testing before mass production.
Bioprinting for Tissue and Organ Fabrication
Bioprinting holds the potential to revolutionize organ transplantation by enabling the creation of functional tissues and organs. While still in the experimental stage, researchers are making significant strides in bioprinting technologies for applications in regenerative medicine.
Transformative Potential for Healthcare
The transformative potential of 3D printing in healthcare lies in its ongoing evolution, technological advancements, and role in shaping the future of personalized and precision medicine.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment
3D printing facilitates the transition toward personalized medicine, where medical interventions are tailored to an individual’s unique anatomy and healthcare needs. This shift enhances treatment efficacy, reduces complications, and improves patient outcomes.
Accessibility to Medical Solutions
As 3D printing becomes more accessible and cost-effective, it has the potential to democratize access to customized medical solutions. It is particularly significant for patients in underserved areas who may benefit from locally produced, patient-specific devices and implants.
Accelerating Medical Innovation
3D printing accelerates medical innovation by providing a versatile platform for researchers and clinicians to explore novel solutions. From drug delivery systems to tissue engineering, the technology fosters a culture of innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in healthcare.
Challenges and Considerations
While 3D printing in healthcare holds immense promise, some challenges and considerations must be addressed for its widespread adoption and ethical use.
Regulatory Frameworks
The regulatory frameworks for 3D-printed medical devices and bioprinted tissues are still in the process of evolving. Establishing clear guidelines and standards is essential to ensure the safety, efficacy, and ethical use of 3D printing technologies in healthcare.
Material Biocompatibility and Safety
Ensuring the biocompatibility and safety of 3D-printed materials is crucial, especially for implants and devices intended for use within the human body. Rigorous testing and validation processes are crucial for mitigating potential risks.
Ethical Considerations in Bioprinting
The ethical implications of bioprinting, particularly in the creation of human tissues and organs, raise important questions about consent, organ ownership, and equitable access. Ethical frameworks must be established to guide the responsible development and use of bioprinting technologies.
Conclusion
3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary force in healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities for customization, innovation, and improved patient outcomes. As the technology continues to evolve, the transformative potential of 3D printing in reshaping the future of medicine is vast. By combining precision, personalization, and accessibility, 3D printing is at the forefront of a healthcare revolution, driving advancements that have the potential to benefit patients worldwide and redefine the practice of medicine as we know it.