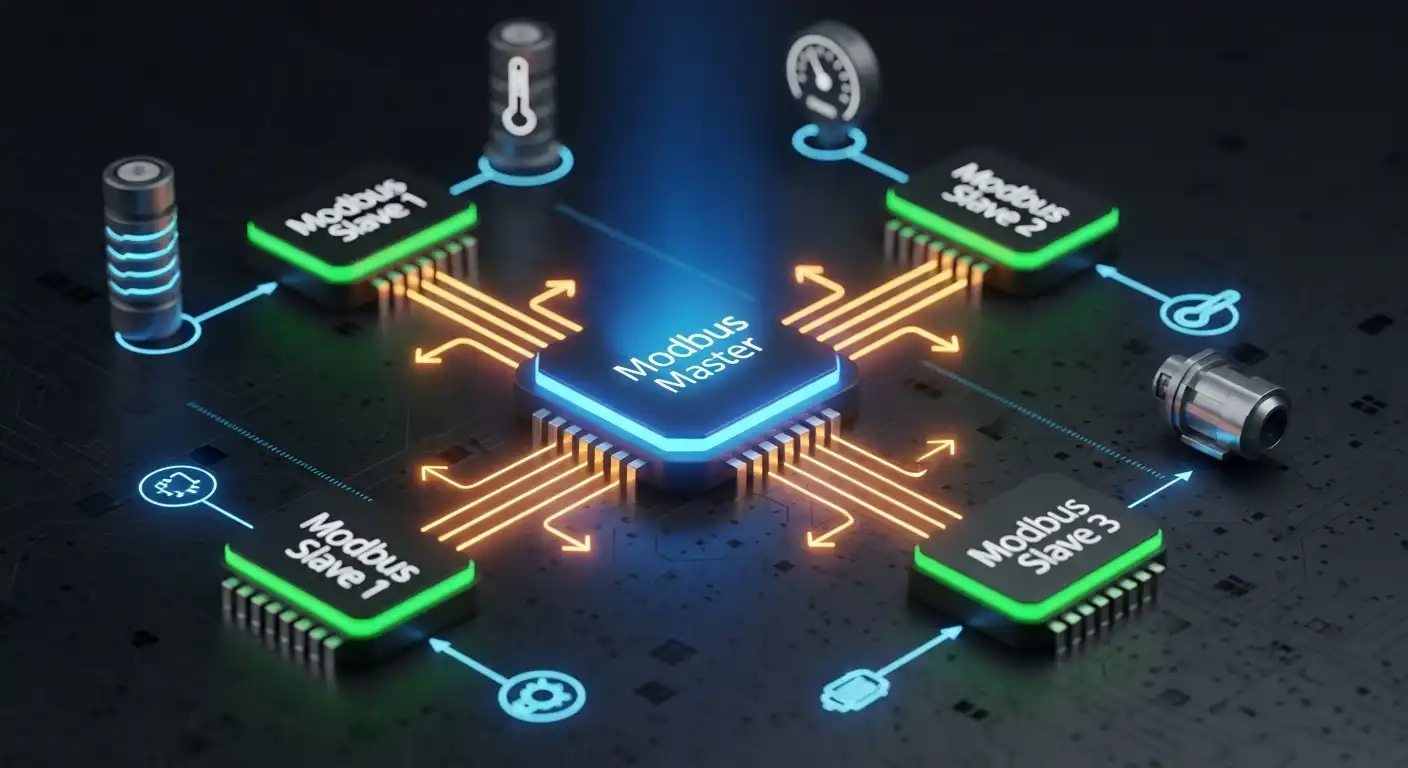
Modbus is a robust and widely used communication protocol in industrial automation systems. Developed in the late 1970s, Modbus has stood the test of time, offering a simple and reliable way for devices to communicate. This article delves into Modbus’s principles, types, benefits, applications, challenges, and future trends, highlighting its significance in industrial communication.
Understanding Modbus
Modbus is a communication protocol used to transmit data over serial lines between electronic devices. It is straightforward to deploy, making it a preferred choice in industrial settings.
What is Modbus?
Modbus is an open protocol that enables devices to communicate over various network types. It is most commonly used for connecting industrial electronic devices. The protocol operates by sending data in packets that include the device’s address, a function code, data, and a checksum for error detection.
History of Modbus
Modbus was developed by Modicon (now Schneider Electric) in 1979 for use with their programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Its simplicity and ease of implementation have led to widespread adoption across various industries, from manufacturing to energy management.
Modbus Protocol Variants
Modbus has evolved into several variants, including Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit), Modbus ASCII, and Modbus TCP/IP. Each variant is suited to different types of communication networks and applications.
Types of Modbus
There are several types of Modbus, each with its unique features and use cases.
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU is the most common variant. It transmits data using binary coding and operates over serial communication lines such as RS-232 or RS-485. Modbus RTU is known for its simplicity and efficiency, making it ideal for real-time control and monitoring applications.
Modbus ASCII
Modbus ASCII uses ASCII characters to encode data, making it readable by humans. It is less efficient than Modbus RTU because it requires more bytes for the same information. However, it is useful in systems where readability and ease of debugging are important.
Modbus TCP/IP
Modbus TCP/IP is a protocol version that uses Ethernet as the physical medium. This variant allows for communication over long distances and integration with modern network infrastructures. Modbus TCP/IP is suitable for applications requiring high-speed communication and internet connectivity.
Benefits of Modbus
Modbus offers several advantages that contribute to its widespread use in industrial automation.
Simplicity and Ease of Implementation
One of Modbus’s primary benefits is its simplicity. The protocol is easy to understand and implement, reducing the complexity and cost of developing communication solutions for industrial devices.
Interoperability
Modbus is an open standard, meaning that devices from different manufacturers can communicate with each other without compatibility issues. This interoperability is crucial in industrial settings where various types of equipment must work together seamlessly.
Flexibility
Modbus can be used over various types of communication media, including serial lines and Ethernet. This flexibility enables it to adapt to diverse network configurations and requirements, making it a versatile choice for industrial communication.
Applications of Modbus
Modbus is used in a wide range of applications across industries, demonstrating its versatility and reliability.
Industrial Automation
Modbus connects PLCs, sensors, actuators, and other control devices in industrial automation. It facilitates real-time monitoring and control of manufacturing processes, improving efficiency and productivity.
Energy Management
Modbus is commonly used in energy management systems to monitor and control electrical devices such as meters, transformers, and circuit breakers. It enables precise measurement and management of energy consumption, contributing to cost savings and sustainability.
Building Automation
In building automation, Modbus integrates HVAC systems, lighting controls, and security systems. It provides a unified platform for managing various building functions, enhancing comfort, safety, and energy efficiency.
Challenges of Modbus
Despite its benefits, Modbus faces several challenges that must be addressed to maintain its relevance in modern industrial communication.
Limited Bandwidth
Modbus RTU and Modbus ASCII have limited bandwidth, making them unsuitable for high-speed data transmission applications. This limitation can be a drawback in scenarios where large amounts of data must be transferred quickly.
Security Concerns
Modbus was designed without built-in security features, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks. The lack of encryption and authentication mechanisms can expose industrial systems to threats, necessitating additional security measures to protect communication networks.
Scalability Issues
Modbus networks can face scalability issues, particularly in large installations. Managing the network and ensuring efficient communication can become challenging as the number of devices increases. Addressing these issues requires careful planning and advanced network management techniques.
Future Trends in Modbus
Modbus’s future is shaped by ongoing advancements and innovative approaches to enhancing its capabilities and addressing its limitations.
Integration with IoT
The integration of Modbus with the Internet of Things (IoT) is a significant trend. IoT platforms can use Modbus to connect and communicate with industrial devices, enabling remote monitoring, control, and data analysis. This integration enhances the functionality and efficiency of industrial systems.
Enhanced Security Measures
As cybersecurity becomes a growing concern, efforts are being made to enhance the security of Modbus communication. Developing secure Modbus variants and implementing encryption and authentication mechanisms are crucial for protecting industrial networks from cyber threats.
Hybrid Communication Systems
Future industrial communication systems will likely employ hybrid approaches that combine Modbus with other protocols and technologies—this hybridization leverages Modbus’s benefits alongside other protocols, creating more robust and versatile communication networks.
Conclusion
Modbus remains a cornerstone of industrial communication, offering simplicity, reliability, and flexibility. By understanding Modbus’s principles, types, benefits, applications, challenges, and future trends, we can appreciate its significant role in facilitating industrial automation and control. Despite bandwidth, security, and scalability challenges, ongoing advancements promise to enhance Modbus’s capabilities and relevance in the ever-evolving industrial communication landscape. As industries continue to adopt and integrate advanced technologies, Modbus will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in driving efficiency, interoperability, and innovation in industrial systems.