Key Points
- Researchers introduced t2 occupancy as a predictive descriptor to enhance nanozyme design.
- The study focuses on chromium-based spinel oxides and identifies optimal activity ranges.
- CuCr2O4 exhibited the highest activity, confirming the descriptor’s reliability.
- The optimized CuCr2O4 nanozyme achieved double the activity of previous materials.
A recent study by Professor Hui Wei and his team has introduced a groundbreaking predictive descriptor, t2 occupancy, to enhance the design of spinel oxide-based nanozymes with superior peroxidase-like (POD) activity. Nanozymes, functional nanomaterials mimicking enzyme properties, have seen growing applications in biosensing, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. However, despite the discovery of thousands of nanozymes, the absence of reliable predictive descriptors has hindered their systematic development.
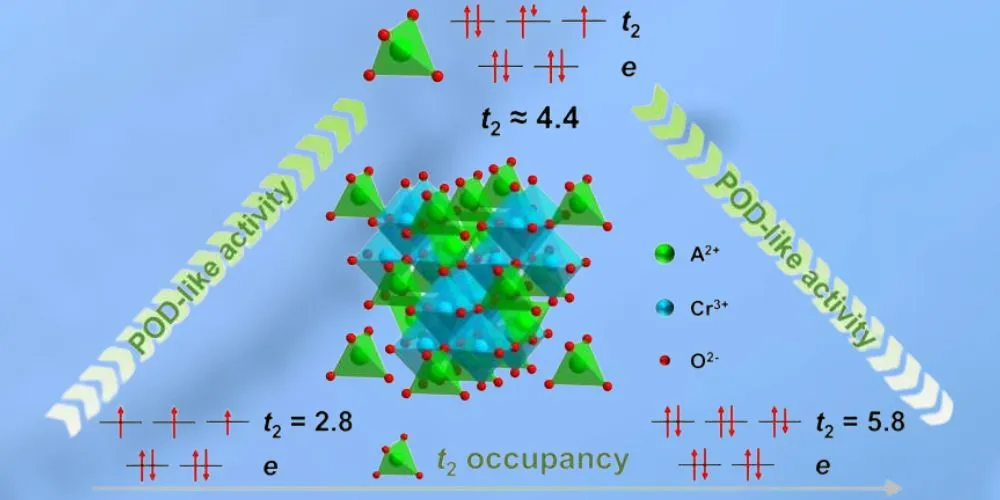
The research published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition highlights how t2 occupancy, a crucial electronic characteristic of tetrahedral crystal sites in spinel oxides, is a reliable tool to optimize POD-like activity. The study focuses on chromium-based spinel oxides (ACr2O4), where different transition metals occupying tetrahedral sites display varying catalytic activities.
By fine-tuning the t2 occupancy and correlating it with activity levels, the researchers identified a “volcanic” trend, with peak activity observed when t2 occupancy values range between 3.7 and 4.9. The material CuCr2O4, with a t2 occupancy of approximately 4.4, demonstrated the highest activity, reinforcing the predictive strength of this descriptor.
Further optimization of the t2 occupancy through precise calcination temperature adjustments resulted in a hundredfold increase in activity compared to earlier materials. To refine the predictive model further, the researchers introduced a dual descriptor approach by incorporating surface oxygen (Oβ) content as a secondary factor. This addition enabled them to achieve better accuracy in activity predictions, particularly when t2 occupancy alone was insufficient. By optimizing both tetrahedral and octahedral sites within the spinel structure, the team surpassed the previously established limitations of the volcanic curve and achieved remarkable performance improvements.
Applying this strategy to the CuCr2O4 nanozyme led to a material with twice the activity of prior benchmarks, representing a major advancement in nanozyme performance. Supported by density functional theory (DFT) calculations, these findings are expected to accelerate the development of high-efficiency nanozymes for various applications.