Key Points
- Integrating AI and machine learning optimizes production and predicts maintenance needs, reducing downtime and costs.
- Modern robots and cobots enhance precision and safety, reshaping the manufacturing workforce. 3D printing enables complex designs and mass customization.
- Developing advanced materials with extraordinary properties using nanotechnology contributes to sustainability and efficiency.
- Increased competitiveness, reduced production costs, and lower carbon footprint are driving sustainable manufacturing practices.
The world is on the cusp of a manufacturing revolution driven by groundbreaking technological advancements. Advanced manufacturing, a term encompassing a variety of innovative techniques and processes, is set to transform industries across the globe, enhancing efficiency, customization, and sustainability. From artificial intelligence and robotics to 3D printing and nanotechnology, the future of manufacturing promises a paradigm shift in how goods are produced and distributed.
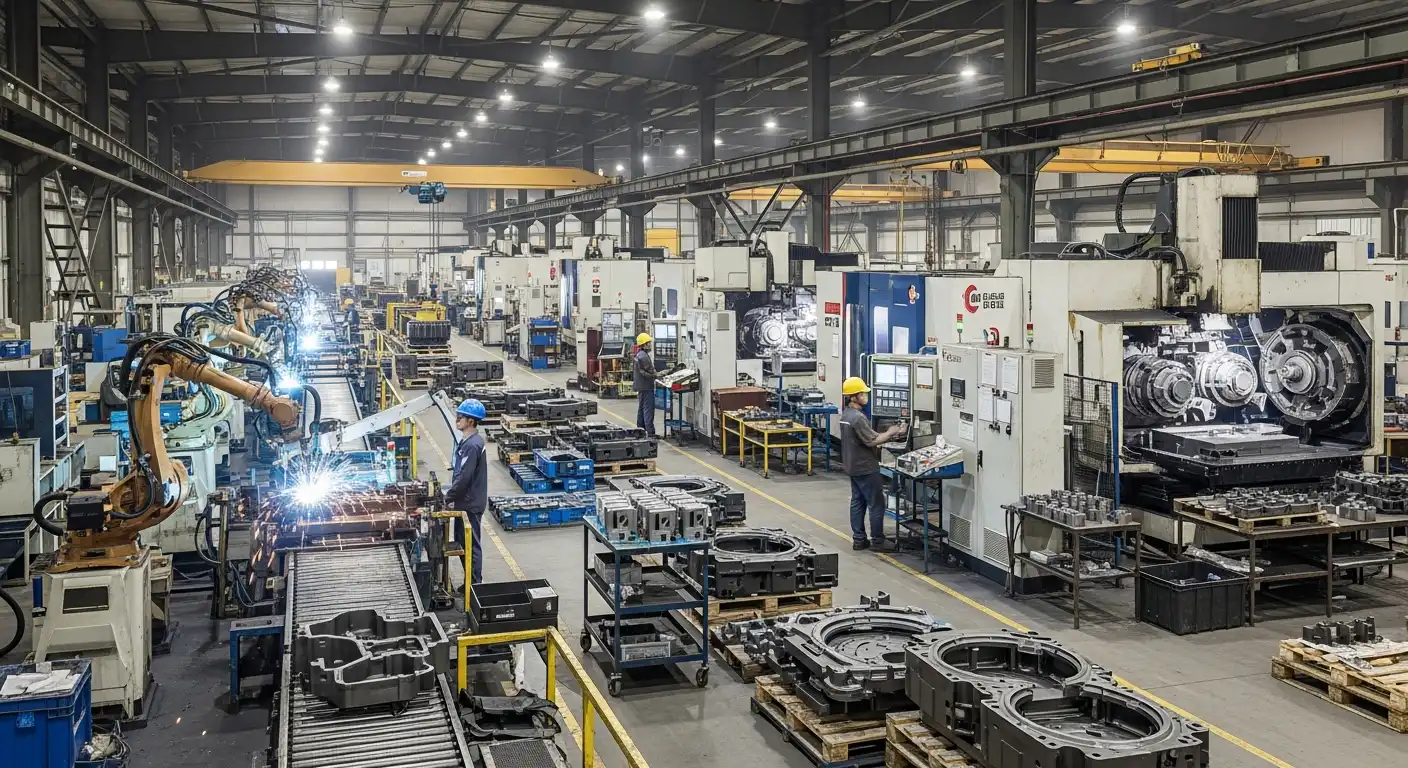
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into production processes is a key pillar of advanced manufacturing. Intelligent manufacturing systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real time, optimize production lines, and predict maintenance needs before they become critical. This predictive maintenance reduces downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery, leading to significant cost savings and improved productivity.
Robotic automation is another critical component. Modern robots, equipped with sophisticated sensors and AI, can perform complex tasks with precision and adaptability. Collaborative robots, or “cobots,” work alongside human operators, enhancing capabilities and ensuring safety in manufacturing environments. This synergy between humans and machines reshapes the workforce, emphasizing the need for new skills and training.
Additive manufacturing, known as 3D printing, revolutionizes product design and production. Unlike traditional subtractive methods, which remove material to create parts, additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer from digital models. This approach allows for unprecedented design flexibility, enabling the creation of complex geometries that were previously impossible to manufacture.
Customization is another significant advantage. Companies can produce tailored products on demand, reducing inventory costs and meeting specific customer requirements. This shift towards mass customization is particularly evident in industries such as healthcare, where personalized medical devices and implants are becoming increasingly common.
Advancements in nanotechnology are opening up new possibilities in material science, enabling the creation of materials with extraordinary properties. Nanomaterials can exhibit enhanced strength, conductivity, and thermal stability, making them ideal for various applications. For instance, carbon nanotubes and graphene are used to develop lighter and stronger materials for the aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
These innovations also contribute to sustainability. Advanced materials can improve energy efficiency, reduce waste, and facilitate recycling. For example, self-healing materials can extend the lifespan of products, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental impact.
The economic implications of advanced manufacturing are profound. By enhancing efficiency and reducing production costs, these technologies can boost competitiveness and drive economic growth. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can also benefit, as lower entry barriers and accessible technologies enable them to compete with larger corporations.
Advanced manufacturing offers significant environmental benefits. Reduced waste, energy-efficient processes, and the ability to produce on demand contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing ecosystem. As industries adopt these technologies, the overall carbon footprint of manufacturing is expected to decline, supporting global efforts to combat climate change.
The future of advanced manufacturing is bright, with ongoing research and development pushing the boundaries of what is possible. As these technologies evolve, they will unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth across various sectors. From personalized healthcare solutions to sustainable energy systems, the impact of advanced manufacturing will be far-reaching and transformative.