Key points
- A new label-free method, Analysis of Tie-lines and Refractive Index, allows for the precise measurement of the molecular composition of biological condensates.
- ATRI can resolve the concentrations of up to five distinct molecules within a single condensate, surpassing the capabilities of previous methods.
- The method combines refractive index measurements with tie-line analysis to determine the composition of condensate.
- ATRI enables more accurate prediction of condensate behavior and understanding of how composition affects biological function.
Biological condensates, membraneless organelles crucial for various cellular processes, have presented a challenge to researchers seeking to quantify their molecular composition. Existing techniques have limitations, particularly in resolving the concentrations of multiple components simultaneously.
A groundbreaking study published in Nature Chemistry introduces a novel method, Analysis of Tie-lines and Refractive Index (ATRI), which overcomes these limitations.
Developed by researchers from Dresden University of Technology, the Leibniz Institute of Polymer Research Dresden, and the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, ATRI offers a label-free approach to determining the precise molecular makeup of these vital cellular structures.
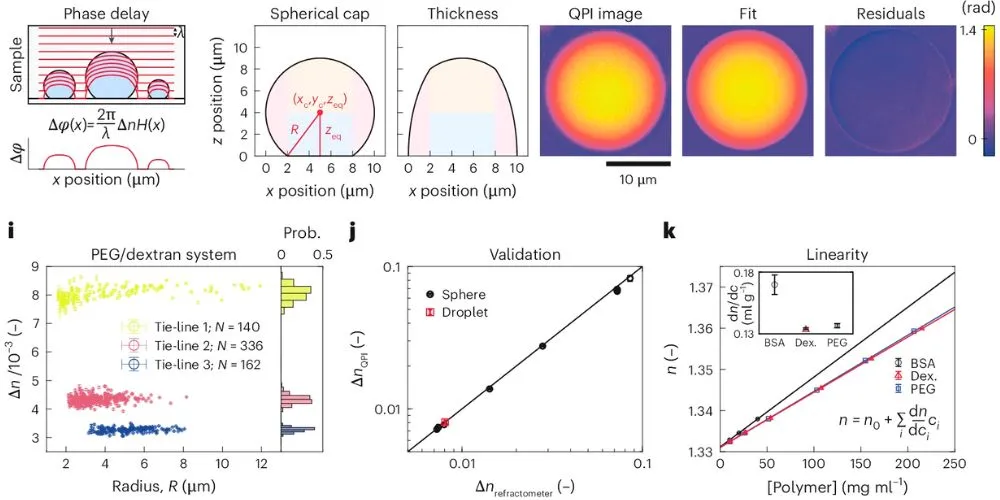
The key innovation of ATRI lies in its combination of refractive index measurements with tie-line analysis. This synergistic approach generates two lines that intersect at a single point, precisely representing the composition of the condensate. This allows for the simultaneous quantification of multiple molecules within the condensate, a feat previously unattainable without the use of fluorescence labeling techniques.
Lead author Dr. Patrick McCall highlights the method’s ability to resolve the concentrations of five distinct molecules, revealing how local composition impacts crucial physical properties such as density and solvent content.
The ability to quantitatively analyze the composition of condensates marks a significant advancement in biological research. ATRI allows for a more accurate prediction of condensate behavior and provides crucial insights into how subtle changes in molecular composition can significantly impact their biological functions. This detailed understanding opens new avenues for research into the fundamental roles of condensates in cellular processes.
Beyond its basic science applications, ATRI holds significant promise for biomedical advancements. Condensates are implicated in numerous diseases, and the ability to precisely measure how their molecular makeup responds to potential therapeutic compounds could revolutionize the field of drug discovery.
By providing a powerful tool to study these complex structures, ATRI paves the way for the development of more effective treatments for a wide range of disorders associated with aberrant condensate formation or function.