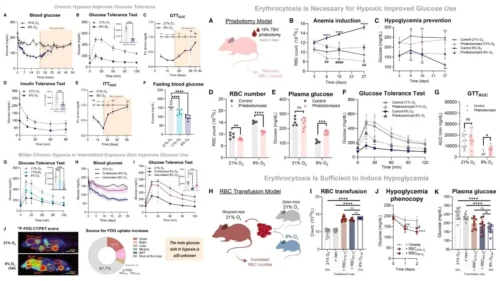
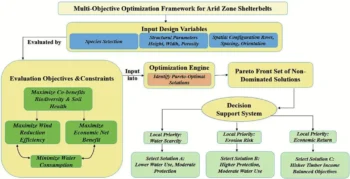
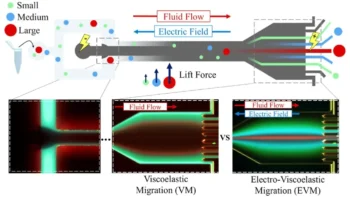
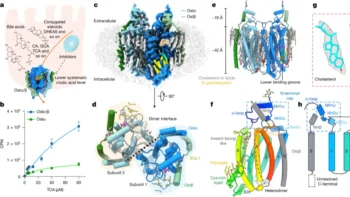
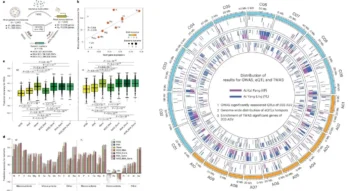
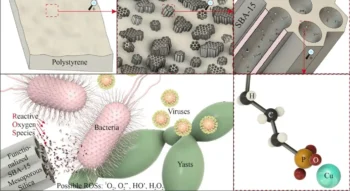
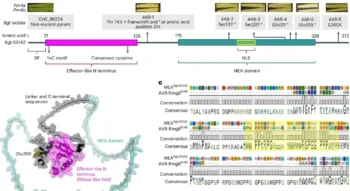
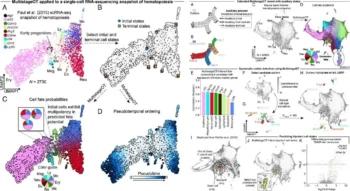
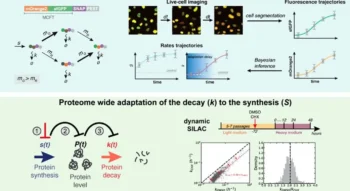
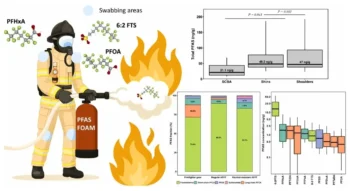
New Study Reveals Red Blood Cells Consume Huge Amounts of Sugar
Key Points: Low oxygen levels drastically lower blood sugar in mice and humans. Red blood cells act as a hidden "sink" for consuming glucose. Hypoxia tricks bone marrow into creating new, sugar-hungry cells. A chemical switch inside the cell speeds...